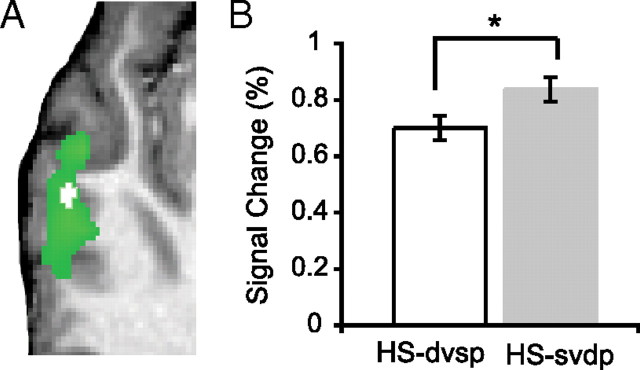
Figure 5.
Subregion of left superior temporal sulcus selective for acoustic–phonetic content of human speech sounds. A, A “masked” analysis restricted to regions identified as HS selective (green) demonstrated an anterior subregion of LmSTS (white) that was selective for the acoustic–phonetic content of human speech stimuli. The mask was defined (and subsequent analysis was performed) using the combined analysis with both trial category and acoustic features considered (p(corr) < 0.001; both models yielded similar results) (see Materials and Methods). Group data are overlaid on anatomical images from a representative single subject. B, The ROI in A was identified as phoneme selective using fMRI-RA; the signal associated with trials in which acoustic–phonetic content was the same (white) was significantly lower than that in trials in which acoustic–phonetic content was varied (gray). The mean ROI signal is depicted here for illustrative purposes only; asterisk indicates significance for voxelwise statistics in A. Error bars indicate SEM.