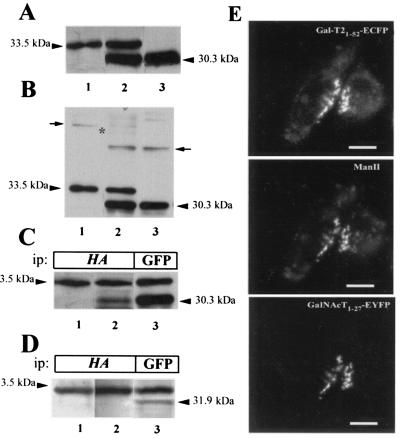
Figure 4.
Expression of EGFP derivative fusion proteins. Membranes from CHO-K1 cells stably expressing Gal-T21–52-HA-ECFP (33.5 kDa, lane 1) or GalNAc-T1–27-EYFP (30.3 kDa, lane 3) or both fusion proteins (lane 2) were subjected to SDS/PAGE in the presence (A) or in the absence (B) of 2-mercaptoethanol and Western blotted with anti-GFP antibody. Arrows in B mark the positions of homodimers, and an asterisk marks the expected position of the band corresponding to heterodimers. (C) Lysates from single Gal-T21–52-HA-ECFP (lane 1) and from double Gal-T21–52-HA-ECFP and GalNAc-T1–27-EYFP (lanes 2 and 3) transfectants were immunoprecipitated (ip) with anti-HA (lanes 1 and 2) or with anti-GFP (lane 3) antibodies, subjected to SDS/PAGE, and Western blotted with anti-GFP antibody. (D) Lysates from single Gal-T21–52-HA-ECFP (lane 1) and from double Gal- T21–52-HA-ECFP and ManII1–76-EYFP (lanes 2 and 3) were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA (lanes 1 and 2) and with anti-GFP (lane 3) antibodies, subjected to SDS/PAGE, and Western blotted with anti-GFP antibody. (E) Visualization of Gal-T21–52-HA-ECFP, endogenous ManII, and GalNAc-T1–27-EYFP. Cells were fixed, immunostained for ManII, and observed under the fluorescence microscope using the filter for EYFP (GalNAc-T), rhodamine (ManII), and ECFP (Gal-T21–52). Bar, 20 μm.