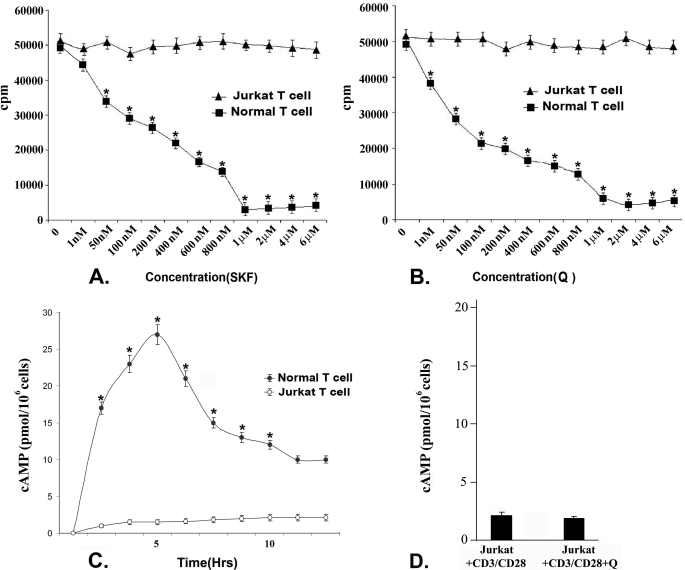
FIGURE 2.
Effect of stimulation of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors on proliferation of activated normal T cells and Jurkat cells by [3H]thymidine incorporation assay. Treated cells were cultured for 72 h, and radiolabeled thymidine was added 18 h before termination of experiments. Incorporated radioactivity was measured as representative of cellular proliferation. Intracellular cAMP concentration also was measured from these treatment groups. A, stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors by its specific agonist (SKF, SKF 82526) in CD3/CD28-stimulated normal T cells showed significant dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation with maximum inhibition found at a 1 μm concentration. In contrast, no significant inhibition of proliferation was observed in CD3/CD28-stimulated Jurkat cells following D1 agonist treatment. B, CD3/CD28-stimulated normal T cells showed significant dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation following stimulation of D2 DA receptors by a specific D2 agonist (Q, quinpirole hydrochloride), and maximum inhibition was found at 2 μm concentration, but no significant inhibition of proliferation was observed in Jurkat cells following D2 DA receptor agonist treatment. Results are mean ± S.E. of six separate experiments (*, p < 0.05). C, intracellular cAMP measured at different time points after D1 agonist stimulation (1 μm) showed a significantly elevated level in normal activated T cells where the peak was reached at 5 h and then declined. But similar treatment failed to elevate intracellular cAMP pool of Jurkat cells. D, stimulation of D2 dopamine receptors could not inhibit the cAMP concentration in CD3/CD28-activated Jurkat cells. Results are mean ± S.E. of six separate experiments (*, p < 0.05). Culture and treatment protocols are as described under “Experimental Procedures.”