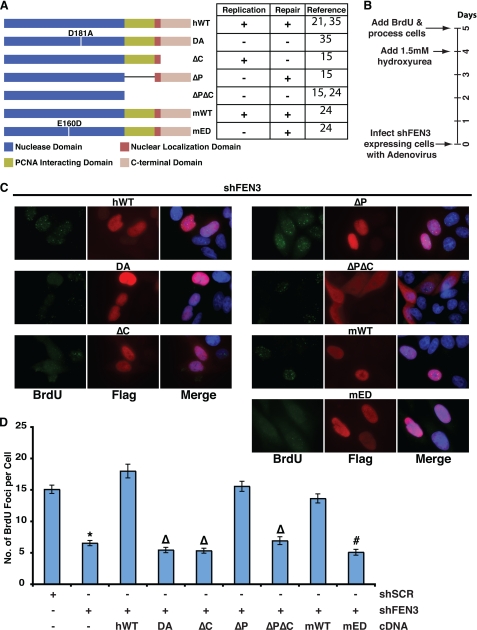
FIGURE 3.
The gap endonuclease activity and C terminus of FEN1 are essential to re-initiate stalled replication forks. A, the schematic shows the different FEN1 alleles used in the study. Inferences on whether the different FEN1 alleles are replication competent or repair competent are shown on the right of the schematic with their associated references. These inferences were made based on nuclease activity and ability to interact with the WRN and PCNA proteins. The mutant proteins are as follows: ΔC (amino acids 360–380 deleted), ΔP (amino acids 337–344 deleted), and ΔPΔC (amino acids 337–380 deleted). B, the timeline of the experimental procedure is given in days. C, representative images show BrdU incorporation after hydroxyurea treatment in FEN1-depleted cells expressing wild-type or FEN1 mutants. Immunofluorescence was conducted using an anti-BrdU (green) antibody, anti-FLAG (red) antibody, and DAPI (blue). D, quantification of the number of BrdU foci per cell in FEN1-depleted HeLa cells with the indicated ectopic FEN1 expression (wild-type or mutant) is shown. Only cells expressing FLAG-tagged FEN1 (marked by red in C) was quantified. No fewer than 75 cells were counted for each condition, and the experiment was conducted twice (a representative experiment is presented). The error bars represent S.E. (*, p < 0.0001 compared with shSCR; Δ, p < 0.0001 compared with hWT; #, p < 0.0001 compared with mWT).