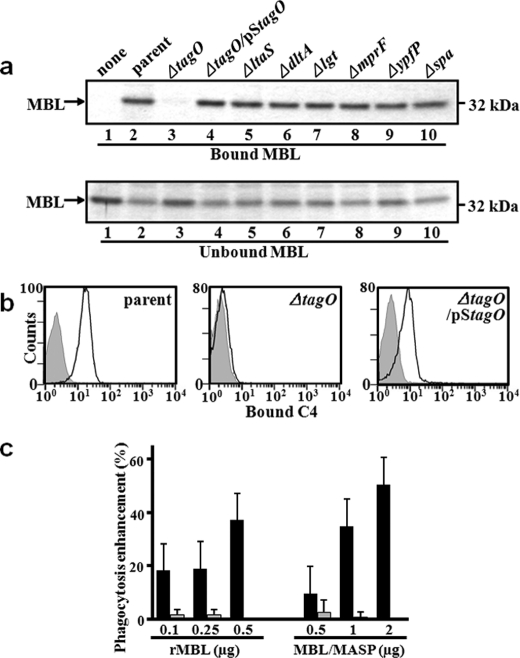
FIGURE 1.
MBL binding to S. aureus cells requires the S. aureus tagO gene. a, screening for a MBL ligand using S. aureus cell wall mutants. Ethanol-fixed S. aureus mutant cells (2.0 × 109 cells) were incubated with rMBL (1 μg), recovered by centrifugation, washed, and the bound MBL was eluted with EDTA-containing buffer. MBL in the eluate (bound) and supernatant (unbound) was detected on 12% SDS-PAGE with CBB staining. S. aureus mutants are described in Table 1 and in the text. Among them, the ΔtagO mutant loses WTA. b, tagO-dependent MBL binding induces C4 deposition on S. aureus cells. S. aureus M0107, T258 (ΔtagO), and T358 (ΔtagO/pStagO) cells (1.0 × 109 cells) were incubated with the MBL/MASP complex (1 μg) at 4 °C for 2 h, washed, and further incubated with C4 (800 ng) at 37 °C for 1 h. Bound C4b on S. aureus cells was detected by flow cytometry (Beckman Coulter) with mouse anti-human C4 mAb and goat F(ab′)2 anti-mouse antibody conjugated with FITC. Gray area represents data without serum. c, tagO-dependent opsonin activity of MBL on S. aureus cells for neutrophils. Ethanol-fixed S. aureus parental (M0107) or ΔtagO mutant (T258) cells labeled with PKH26 (1.0 × 106 cells) were incubated with rMBL (250 ng) or MBL/MASP complex (1 μg) at 4 °C for 2 h. Bacterial cells were washed, and further incubated with human neutrophils labeled with PKH67 (1.0 × 105 cells) at an MOI of 10:1 at 37 °C for 1 h. The phagocytosis of S. aureus cells by neutrophils was analyzed by flow cytometry. The opsonin activity of rMBL or MBL/MASP is shown as relative increase in phagocytosis of S. aureus cells by neutrophilis.