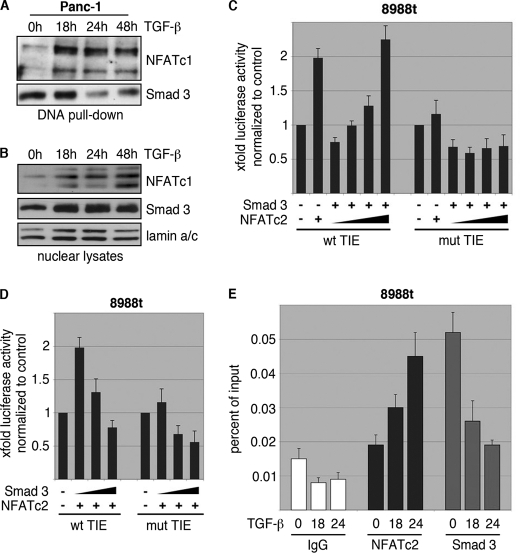
FIGURE 7.
NFAT displaces Smad3 from the c-Myc/TIE upon TGF-β. A, DNA pulldown experiment demonstrating inverse binding of NFAT factors and Smad3 on the c-Myc/TIE upon TGF-β. Nuclear extracts from Panc-1 cells were prepared and incubated with the wild-type c-Myc/TIE oligonucleotide sequence. DNA-protein complexes were precipitated with streptavidin-agarose beads, and NFAT/Smad3 binding was analyzed by Western blotting using anti-NFATc1 and anti-Smad3 antibodies, respectively. Note the inverse binding of NFAT factors and Smad3 on the c-Myc/TIE sequence upon treatment with TGF-β. B, nuclear extracts which were used for DNA pulldown experiments. C and D, reporter gene assay shows that c-Myc/TIE promoter induction depends on the integrity of the NFAT binding site and the amount of NFAT and Smad3. PaTu8988t cells were transfected with c-Myc/TIE wild type or c-Myc/TIE mutant that lacks the NFAT binding site along with increasing amounts of either NFATc2 (C) or Smad3 (D). c-Myc promoter activities were expressed as mean fold induction. Mean value were calculated from three independent experiments and are shown as mean ± S.D. E, chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed in PaTu8988 cells following TGF-β treatment over 18 and 24h using specific NFATc2 and Smad3 antibodies. In vivo binding of both transcription factors to the c-Myc promoter was determined by quantitative PCR using primers specific for the c-myc promoter region harboring the c-Myc/TIE. ChIP assay demonstrates inverse binding of Smad3 and NFAT to the c-Myc/TIE upon TGF-β.