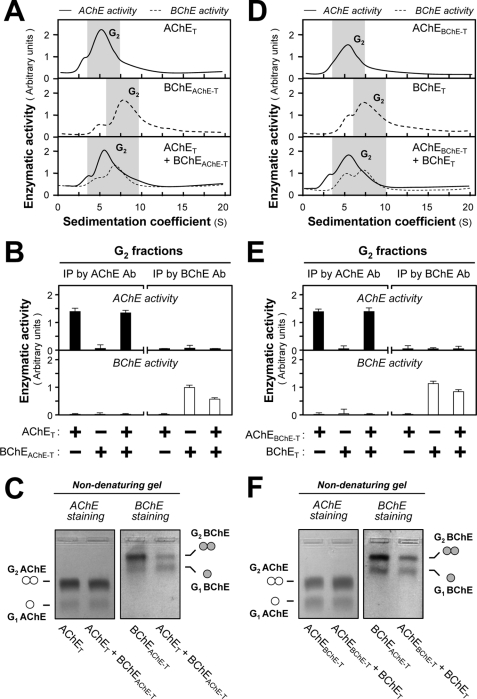
FIGURE 6.
AChE and BChE subunits do not form hybrid dimers, even when they contain the same t-peptide. A and D, HEK293T cells were single or double transfected with cDNAs encoding AChE and BChE catalytic subunits, which contained the same t-peptides (AChET and BChEAChE-T or AChEBChE-T and BChET). Sucrose density gradient analysis was performed as in Fig. 1A. B and E, G2 fractions from single and double transfected cells (shaded in A and D) were immunoprecipitated by either anti-AChE or anti-BChE antibodies and absorbed on protein G beads. The enzymatic activities of AChE and BChE immobilized on the beads were determined. C and F, G2 fractions from single and double transfected cell lysates (shaded in A and D) were analyzed by nondenaturing electrophoresis coupled with Karnovsky staining as in Fig. 2. The absence of hybrid dimer in the double transfection indicates that AChE and BChE subunits do not associate, even when containing the same t-peptide. The enzymatic activities are expressed in arbitrary units. The values are the means ± S.E., each with triplicate samples (n = 3). Representative gradient profiles and gels are shown (n = 4). Ab, antibody; IP, immunoprecipitation.