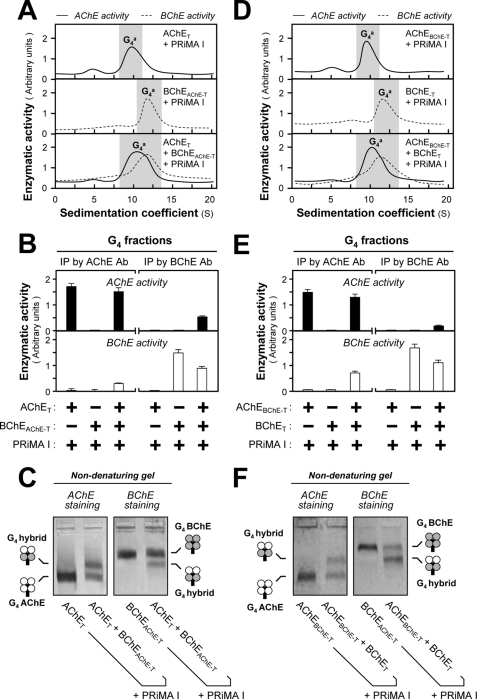
FIGURE 7.
Formation of G4 hybrids by AChE and BChE subunits containing the same t-peptide. A and D, HEK293T cells were single or double transfected with cDNAs encoding AChE and BChE catalytic subunits, which contained the same t-peptides (AChET and BChEAChE-T or AChEBChE-T and BChET) together with cDNA encoding PRiMA I. The amount of PRiMA I cDNA was doubled in the triple transfection. Sucrose density gradient analysis was performed as in Fig. 1A. B and E, G4 fractions from single and double transfected cells (shaded in A and D) were immunoprecipitated by either anti-AChE or anti-BChE antibody and absorbed on protein G beads; the retained AChE and BChE activities were determined by Ellman assays. C and F, analysis of G4 fractions from double and triple transfected cells by nondenaturing electrophoresis coupled with Karnovsky staining as in Fig. 2. The presence of a new oligomer migrating between G4 AChE and G4 BChE indicates that AChE and BChE, possessing the same t-peptides, can form a PRiMA-linked G4 hybrid. The enzymatic activities are expressed in arbitrary units. The values are the means ± S.E., each with triplicate samples (n = 3). Representative gradient profiles and gels are shown (n = 4). Ab, antibody; IP, immunoprecipitation.