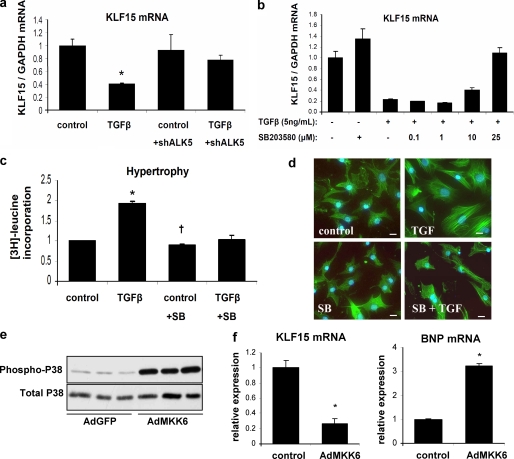
FIGURE 2.
In vitro activation of p38 MAPK is both necessary and sufficient to decrease KLF15 levels. a, TGFβ regulates KLF15 expression in vitro. Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were infected with a lentivirus containing shRNA against ALK5 or with a control lentivirus. TGFβ decreased expression of KLF15 after control virus but had no effect in the cells treated with the shRNA. (n = 3/group; *, p < 0.01 compared with control group; †, p < 0.01 compared with TGFβ-treated cells without shRNA against ALK5. b, specific inhibitor of p38 MAPK, SB203580, abolishes the TGFβ-induced down-regulation of KLF15 in cardiomyocytes in a dose-dependent manner. c, inhibition of p38 MAPK prevents TGFβ-induced hypertrophy, measured by [3H]leucine incorporation (n = 3/group; *, p < 0.05 compared with control group; †, p < 0.05 compared with TGFβ-treated cells without SB203580 (SB) treatment), and d, inhibition of p38 MAPK prevents TGFβ-induced increase in cell size as visualized by phalloidin staining of F-actins. Bars in panels represent 50 μm. e, Western blot analysis shows an increase in phosphorylated p38 MAPK after infection of cardiomyocytes with constitutively active adMKK6, the upstream kinase of p38. f, adenoviral overexpression of MKK6 resulted in decreased KLF15 mRNA levels and increased expression of the hypertrophy marker BNP (n = 3/group; *, p < 0.05 compared with control group).