Figure 3.
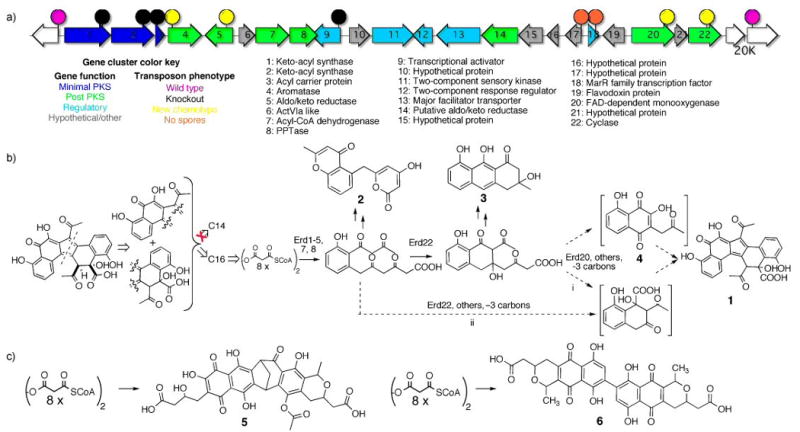
a. The Erd gene cluster (GenBank accession number FJ719113) and the location of key transposon insertions discussed in the text. b. A retrobiosynthetic analysis of erdacin suggests that it might arise from two 13-carbon monomers, however, only 16-carbon compounds accumulate in transposon knockouts of early post miminal PKS genes. A proposed biosynthetic scheme for the formation of erdacin from an octaketide precursor is shown. Compounds 1-4 were isolated from wild type and mutant V167 cultures. Shown in brackets are juglomycin F (4) and a hypothetical 13-carbon polyketide which together have carbon skeletons that accout for the upper and lower halves of erdacin, respectively. c. The Erd minimal PKS genes are related to minimal PKS genes involved in the biosynthesis of the two structurally distinct octaketide dimers naphthocyclinone (5) and actinorhodin (6).
