Fig. 2.
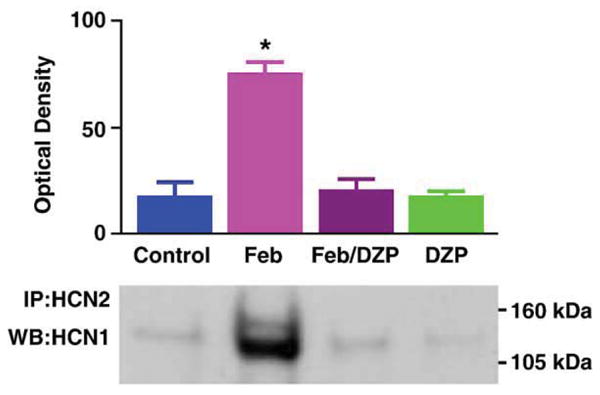
Hyperthermic (febrile) seizures rather than the elevation of brain temperature per se are required for increased HCN1/HCN2 co-association. To dissociate ‘fever’ from ‘febrile seizures’, rats sustaining hyperthermia were pre-treated with the benzodiazepine diazepam (DZP; 10 mg/kg) to block the seizures. As shown, HCN1/HCN2 co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) was increased in hippocampi of rats sustaining seizures (Feb), but not in those from hyperthermic rats that did not have seizures (Feb/DZP) or in the normothermic, diazepam-treated group (DZP). * Significantly different from controls (P = 0.01).
