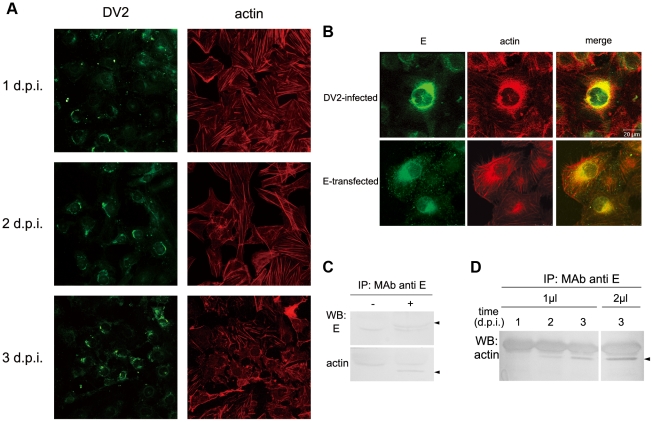
Figure 6. The association of DV2 E proteins with actin in infected cells.
A. Reorganizations of actin cytoskeleton induced by DV2 infection. ECV304 cells were infected with DV2 at 37°C for 1 h, and fixed at different time points (1, 2, and 3 d p.i.). Then cells were labeled with mouse anti-DV2 PAb and TRITC-phlloidin, followed by FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. ×400. B. Actin filaments are co-localized with E protein in DV2-infected and E-transfected ECV304 cells. The cells were fixed at 24 h p.i. or 48 h post transfection, and double-labeled with a mixture of MAbs 301 and 504, followed by FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (left panels), and phalloidin-TRITC (middle panels). Merged images are given in the right panels. (Bar 20 µm). C. Co-IP of DV2 E protein with actin filaments. At 3 d p.i., cell lysate were immunoprecipitated with anti-E antibodies (a mixture of MAbs 301 and 504) followed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblot analysis with anti actin PAb or anti DV2 PAb separately. Arrowheads on the right indicate DV2 E protein (top) and actin (bottom). D. The amount of E protein immunoprecipitated with anti-actin antibodies was increased with the progression of infection. Co-IP assays were carried out with 1 µl of a mixture of MAbs 301 and 504 at 1, 2, and 3 d p.i., or with 2 µl of a mixture of MAbs 301 and 504 at 3 d p.i. The immunoprecipitated actin was detected with anti actin PAb.