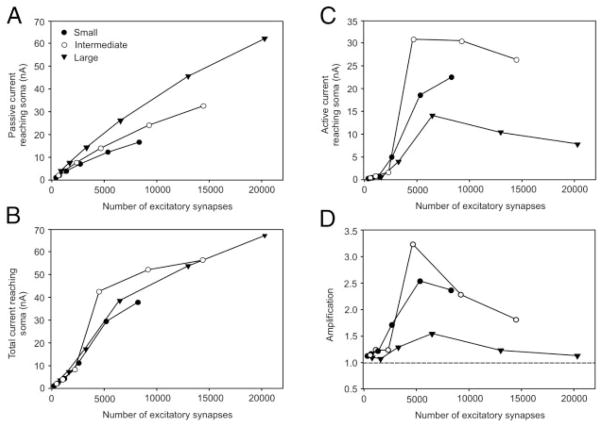
FIG. 6.
Current reaching soma caused by activation of PICs and excitatory synaptic activity. Somatic membrane potential was clamped at − 64 mV. Excitation levels were varied by activating 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 100% of maximum number of excitatory synapses. These excitation levels were converted to an absolute number of synapses to examine somatic current for a given amount of synaptic input. A: passive condition. Models do not contain voltage-dependent channels on dendritic tree. B: active condition. Models contain L-type Ca2+ channel hotspots on dendrites and are positioned according to Fig. 1. Total current reaching soma is comprised of both passive and active currents. C: current reaching soma from PICs. This was determined by taking difference between total and passive currents in A and B. D: amplification of synaptic of current caused by PIC activation as a function of excitation level. Gray dashed line at 1.0 indicates no amplification. Closed circles, DVS 25–2, small motoneuron; open circles, DVS 25–3, intermediate-sized motoneuron; triangles, DVS 14–1, large motoneuron.