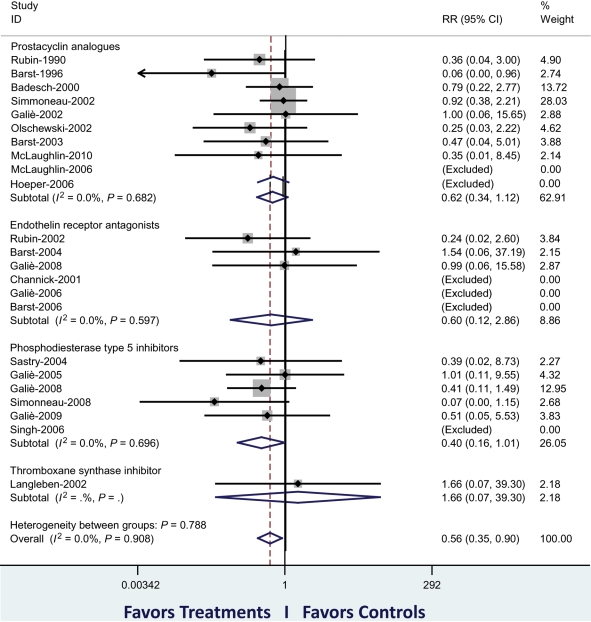
Figure 4.
Meta-analysis of published randomized controlled studies (identified by first author and year of publication) in pulmonary arterial hypertension as of May 2010. The primary analysis has included 3780 patients of 23 trials. The figure shows the cumulative RR estimate of death in active treatment groups when compared with control groups stratified according to treatment class (inverse variance method). Studies with no events in both groups were excluded. An overall reduction of mortality of 44% (P = 0.016) is shown. The sensitivity analysis, including two additional studies (59 patients) in which two treatment strategies were compared, confirmed a reduction in mortality of 39% (P = 0.041). The subgroup analysis of the three classes of approved drugs achieved a similar favourable reduction in mortality, although no statistical significance was achieved individually. RR, relative risk. Modified from Galiè et al.12