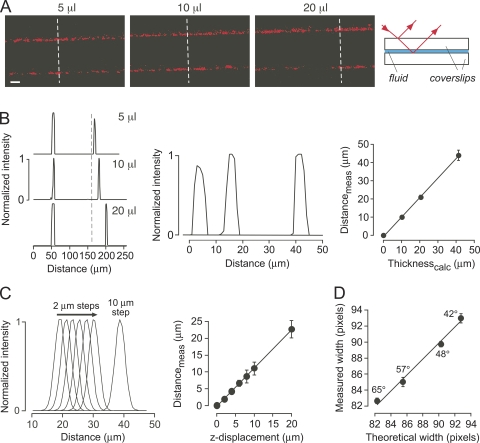
Figure 2.
Surface reflectance validation and resolution. (A) SLRM images of fluid layers (volumes, 5, 10, and 20 µl) sandwiched between cover glasses. (Right) Schematic showing origin of the reflections. (B; left) Corresponding intensity versus distance profiles measured at dashed white lines in A. (Middle) Distance-expanded view of second reflections. (Right) Fluid thickness computed from fluid volume added (Thicknesscalc) as a function of fluid thickness measured by SLRM (Distancemeas). Mean ± SEM of five measurements per cover glass with linear regression (r2 = 0.99). (C; left) Intensity versus distance profiles for reflections from a cover glass, with 2-µm displacements in the z-direction. (Right) Corresponding computed displacements (Distancemeas) against actual z-displacement. Mean ± SEM of five measurements. (D) Measured width in pixels (8× magnification) between reflections for a 100-µm-thick cover glass as a function of incident light angle versus theoretical width calculated from incident light angle, and cover glass thickness (78 pixels) and refractive index. Mean ± SEM of three measurements.