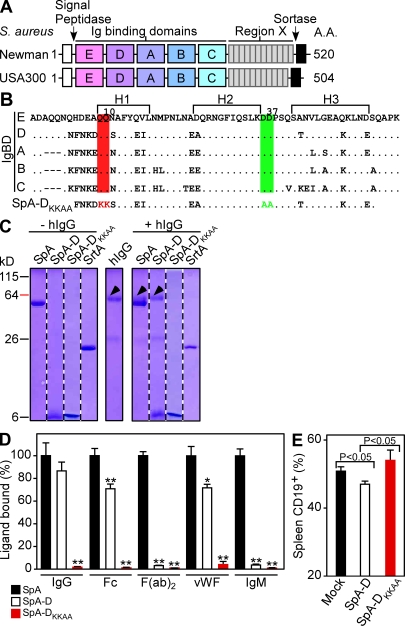
Figure 1.
Generation of a nontoxigenic SpA vaccine. (A) SpA of S. aureus Newman and USA300 LAC harbors an N-terminal signal peptide (white boxes), five Ig binding domains (E, D, A, B, and C), variable region X, and C-terminal sorting signal (black boxes). (B) Amino acid sequence of the five Ig binding domains, as well as nontoxigenic SpA-DKKAA, with the positions of triple α-helical bundles (H1, H2, and H3), as well as glutamine (Q, red) 9 and 10 and aspartate (D, green) 36 and 37 as indicated. (C) Coomassie blue–stained SDS-PAGE of SpA, SpA-D, SpA-DKKAA, or sortase A purified on Ni-NTA sepharose in the presence or absence of human immunoglobulin (hIgG). (D) ELISA examining the association of immobilized SpA, SpA-D, or SpA-DKKAA with human IgG, as well as its Fc or F(ab)2 fragments, vWF and IgM. Statistical significance of SpA-DKKAA binding to each ligand was compared against SpA-D, and SpA-D binding was compared against SpA (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (E) CD19+ B lymphocytes in splenic tissue of 6-wk-old BALB/c mice (n = 6) that had been mock immunized or treated with SpA-D or SpA-DKKAA were quantified by FACS. Data are the means and error bars represent ±SEM. Results in C–E are representative of three independent analyses.