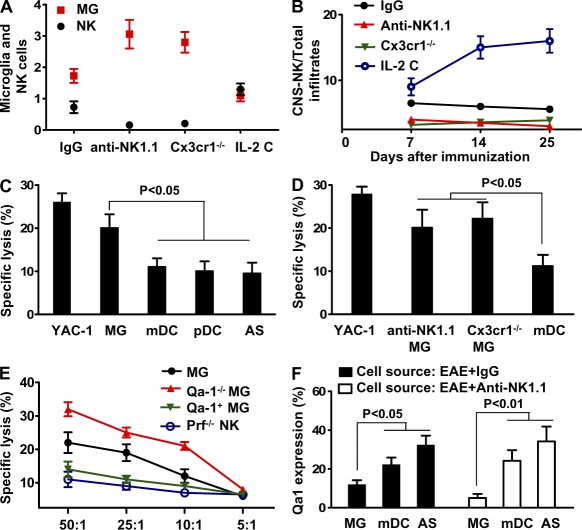
Figure 7.
Missing self on microglia breaks NK cell tolerance. (A and B) Inverse relationship between NK cells and microglia. CNS infiltrates were isolated from MOG/CFA-primed Cx3cr1 GFP+/− mice after treatment with control IgG, anti-NK1.1 mAb, or IL-2 complexes. (A) Numbers of NK cells (×105) and GFP+ microglia (×106) that were analyzed by FACS. (B) Ratio of CNS-resident NK cells and total CNS infiltrates. P < 0.01 for comparisons of microglial cell numbers from each experimental group with that from control mice. P < 0.01 for comparisons of the ratios of CNS-derived NK cells/total infiltrates from the groups that received IL-2 C with that from the remaining groups. P < 0.05 for comparisons between groups of mice that received IgG and groups that received anti-NK1.1, or groups of Cx3cr1−/− mice. (C) NK cells principally target microglia. NK cells were purified from pools of CNS tissues harvested from MOG-immunized mice treated with IL-2 complexes. Microglia, astrocytes, mDCs, and pDCs were isolated from MOG-primed Cx3cr1+/− mice and incubated with 51Cr. The effector (NK) and target (microglia) cells (5 × 104) were incubated at E:T ratios of 25:1 and cytolytic effects were measured in a 4-h 51Cr-release assay, as previously described (Shi et al., 2000). (D) Microglia, astrocytes, and mDCs were isolated from MOG-primed Cx3cr1+/− mice or Cx3cr1−/− mice and incubated with 51Cr. The effector (NK) and target (5 × 104) cells were transferred into RAG1−/−γc−/− mice and a rapid elimination assay (see Materials and methods) was performed. (E) Role of the NKG2A–Qa1 pathway in the interaction between NK cells and microglia. Cytotoxicity assay was conducted with effector NK cells from MOG/CFA-primed WT or perforin-deficient mice. Target cell microglia were isolated from Cx3cr1+/− mice, Qa1/Cx3xr1 double-deficient mice (Qa1−/− MG), or with microglia overexpressing Qa1 (Qa-1+ MG). MG denotes microglia isolated from MOG/CFA-primed Cx3cr1−/− mice. Qa1+MG denotes overexpression of Qa1 on microglia from Qa1−/− mice (see Materials and methods). Data regarding the killing activity of NK cells from the CNS of WT animals with EAE were not available, as it was technically challenging to purify sufficient numbers of NK cells to perform the assay. (F) Expression of Qa1 on CNS-derived APCs in the presence or absence of NK cells. CNS-derived cells (days 12–20 after immunization) from MOG-immunized mice treated with IgG or anti-NK1.1 were analyzed for Qa1 expression by FACS. All data are representative of two to three independent experiments with 12–18 mice per group each (mean ± SEM). P-values were determined by an ANOVA test.