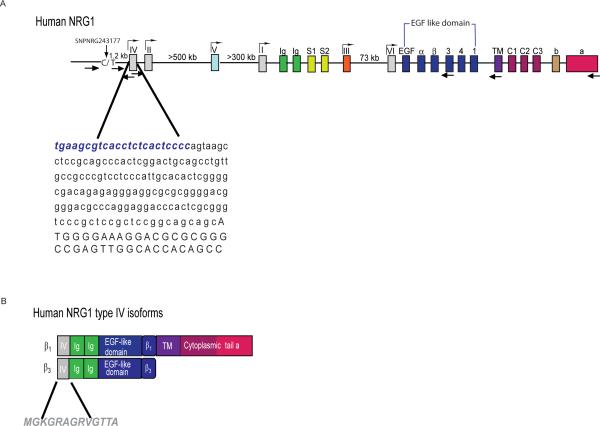
Fig 1. Mapping the NRG1 type IV promoter and isolation of type IV transcripts.
A) Genomic organization of NRG1 showing putative promoters and exons encoding distinct functional domains. The exons are represented by different color boxes, and putative promoters (exons I through VI) are indicated (gray boxes). Exons encoding the different domains are color-coded and represent: Ig-like domain (green), spacers (cyan), α and β EGF-like domains splice variants with extensions 1–4 (blue), TM (purple), cytoplasmic domains 1–3 (bourdeaux), and the distinct C-termini a and b (orange). Sites and orientations of primers used in this study are indicated by the arrows below. The sequence of the type IV exon is shown, including the novel upstream 23 bp sequence identified in this study (bold blue). Location of the 8NRGSNP243177 polymorphism is indicated. (B) Schematic representation of the human type IV isoforms encoded by the cDNAs isolated in this study (β1and β3). The domains contained in each protein, as defined in the diagram above, are shown. The unique 13 amino acid type IV human sequence used to generate a type IV specific antibody is shown below.