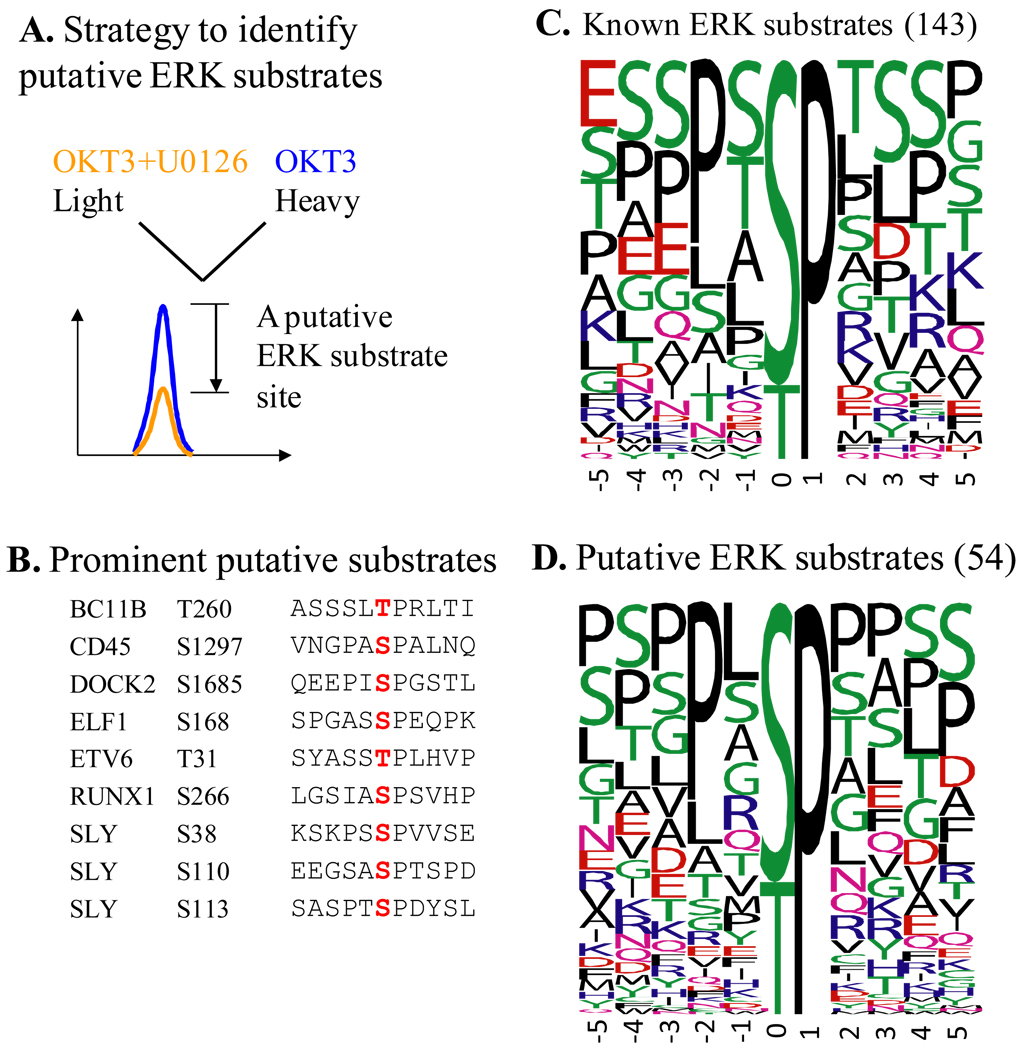
Figure 2. Putative substrates of ERK during the initial phase of TCR signaling defined by quantitative phosphoproteomics.
(A) Stable Isotope Labeling of Cells in culture (SILAC) strategy was used to define TCR-responsive phosphorylation sites that are ERK-dependent, or in other words are ERK substrates. U0126 is a widely used, specific inhibitor of Mek kinases whose only known function is to activate ERK kinases. OKT3 is a functional antibody specific for CD3ε, which is used to crosslink CD3 coreceptors and initiate TCR signaling. Phosphopeptides that showed a >1.9 fold decrease in their abundance due to the inhibitor and harbored proline-directed phosphorylation sites were considered to contain substrate sites of ERK. (B) Putative substrates of ERK on seven proteins that are known to be involved in TCR signaling or are only found in lymphocytes. Residues marked in red are the actual substrate sites. (C) and (D) Frequency plots of residues surrounding known (C) and putative (D) substrate sites of ERK defined in the current study. The height of the residues represents the frequency with which they occur at the respective positions relative to the substrate site (designated 0 by convention) of phosphorylation. The color of the residues represents their physico-chemical properties. Note the preference for Pro and Leu in the −2 position in both the known and putative substrates of ERK. Also note the overall predominance of Ser, Thr, Pro, and Leu around the phosphorylation site. The frequency plots were generated with WebLogo (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/). Among the 54 putative substrates from this study, Ser25 of stathmin and Ser266 of RUNX1 are known substrates of ERK. Known substrate sites were retrieved from the phosphoELM database. This figure is adapted from Mayya et al. (2009) [23].