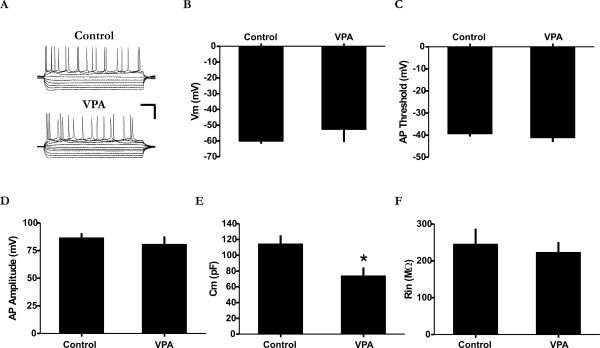
Figure 5.
Intrinsic membrane properties between control and VPA-treated neurons. VPA-treatment does not appear to result in the abnormal electrophysiological development of TeA neurons. A: Recordings from a neuron obtained from a control (top) and VPA-treated animal (bottom) illustrating a similar voltage response to current injection. Scale bars = horizontal 100 ms; vertical 40 mV. B-F: Comparison of five basic intrinsic membrane properties. B, resting membrane potential; C, action potential threshold; D, action potential amplitude; E, membrane capacitance; and F, input resistance. The membrane capacitance was slightly smaller in neurons of VPA-treated animals although it is still significantly larger than immature neurons and comparable to those obtained from control animals (not shown). Data are from animals of similar age. * p < 0.05.