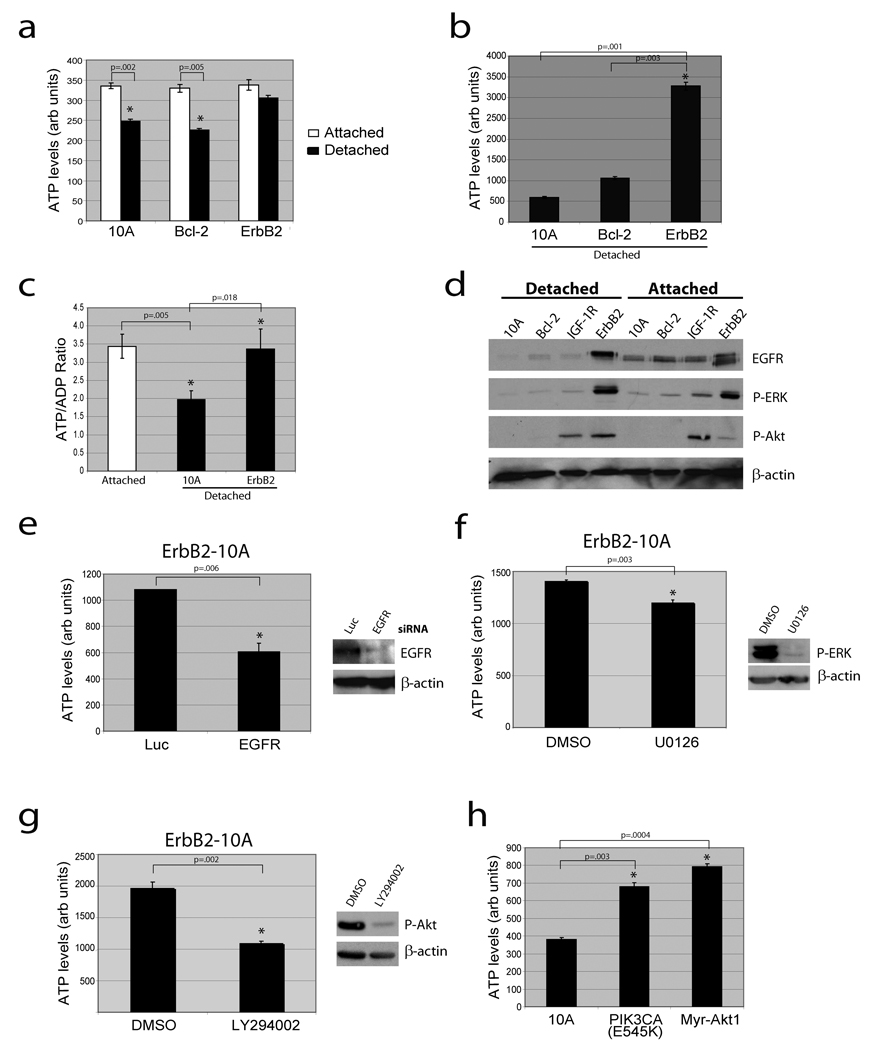
Figure 1. Loss of matrix attachment causes reduction in cellular ATP that is rescued by ErbB2 through PI(3)K pathway activation.
(a) ATP was measured in the indicated cells 24 hours after plating in adherent or non-adherent (poly-HEMA-coated) plates using the ATPlite assay (a) or the ATP determination kit (b). (c) The ATP/ADP ratio was measured in the indicated cells. (d) The indicated cells were immunoblotted for EGFR, p-ERK, p-Akt, or β-actin. IGF-1R cells were used as a positive control for p-Akt. (e) ErbB2-MCF-10A cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting luciferase (luc) or EGFR and ATP levels were measured using the ATP determination kit. Knockdown was confirmed by immunoblot. (f) and (g) Detached ErbB2-MCF-10A cells were treated with 10 µM UO126 (ERK pathway inhibitor) (f) or 50 µM LY294002 (PI(3)K inhibitor) (g) for 24h and ATP was measured using the ATP determination kit. Inhibition was confirmed by immunoblotting. (h) ATP was measured in detached 10A cells or 10A cells expressing PIK3CA (E545K) or Myr-Akt1 using the ATP determination kit. All error bars represent standard deviation (n=3). A * represents a statistically significant change calculated using a 2 tailed t test.