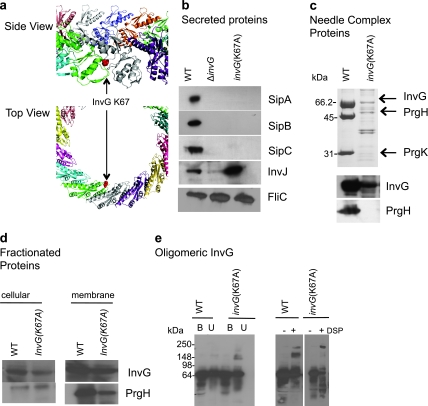
FIG 3 .
InvG affects substrate switching. (a) InvG ring model, with each InvG monomer shown in a different color, with the Lys67 residue highlighted in red. (b) Effect of InvG(Lys67Ala) on type III secretion profiles. Secreted proteins for the invG(Lys67Ala) strain were Western blotted with monoclonal antibody to the effector SipA and transclocon components SipB and SipC and polyclonal antibody against the needle length regulator protein InvJ. Secreted proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using an antibody against the flagellin protein FliC to control for loading. (c) Effect of InvG(Lys67Ala) on type III needle complex assembly. Wild-type and mutant needle complexes were isolated and separated by SDS-PAGE and Western blotted with antibodies to InvG and PrgH. (d) Effect of InvG(Lys67Ala) on type III ring components. Cellular and membrane fractions isolated from S. Typhimurium were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against InvG and PrgH. (e) Effect of InvG(Lys67Ala) on the assembly of the InvG oligomer. Outer membrane fractions from E. coli C41 cells expressing InvH and wild-type InvG or InvG(Lys67Ala) were isolated. Samples were boiled in sample buffer (B) or subjected directly (U) to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibody against InvG. Samples were also incubated with or without the cross-linker DSP (dithiobis[succinimidyl propionate]) for 60 min at 22°C prior to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibody against InvG.