FIG. 1.
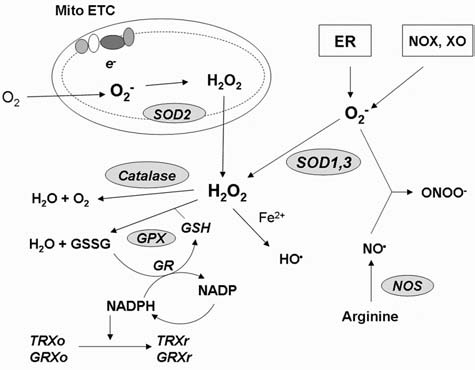
Redox homeostasis. Major sites of cellular ROS generation include the mitochondrial electron transport chain (Mito ETC), the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) system, and the NAD(P)H oxidase (NOX) complex. Nitric oxide synthases (NOS) are key enzymes for production of NO. Major ROS-scavenging enzymes are highlighted in grey. GSH and NAPDH play roles in maintaining the reduced cellular redox state. GPX, glutathione peroxidase; GR, glutathione reductase; TRXo, thioredoxin (oxidized); TRXr, thioredoxin (reduced); GRXo, glutaredoxin (oxidized); GRXr, glutaredoxin (reduced); HO·, hydroxyl radical; NO·, nitric oxide; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; XO, xanthine oxidase.
