FIG. 5.
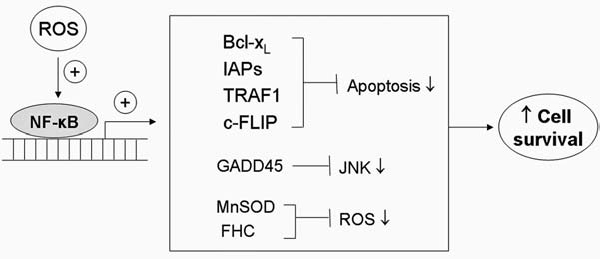
Role of NF-κB in cell survival. NF-κB functions as a transcription factor regulating the expression of multiple genes. Activation of NF-κB by stimuli such as oxidative stress or cytokines promotes increased expression of antiapoptotic proteins such as Bcl-xL and XIAP, which suppress the execution phase of cell death. Induction of GADD45 leads to inhibition of JNK and prevents JNK-induced apoptosis. NF-κB also promotes the expression of antioxidant genes such as MnSOD, which plays a major role in scavenging mitochondria superoxide and in maintaining redox homeostasis. Overall, the activation of NF-κB by ROS leads to inhibition of apoptosis, redox rebalance, and enhanced cell survival.
