FIG. 8.
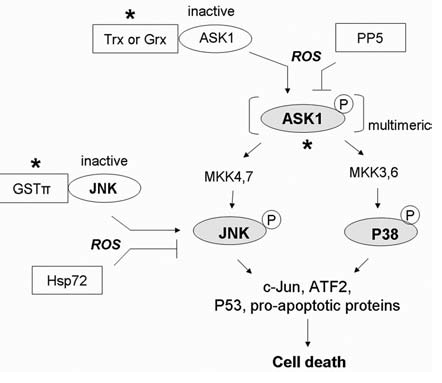
Redox regulation of stress-responsive kinase (SAPK) signaling pathways. In most cases, activation of the SAPK pathway transduces an oxidative stress signal to cell death. Under nonstressed conditions, apoptosis-regulating signal kinase 1(ASK1) is inhibited by the reduced form of thioredoxin (Trx) or glutaredoxin (Grx). Increased oxidative stress causes oxidation of Trx and Grx and releases ASK1 to form an active multimeric complex with proper trans- or autophosphorylation. The activation of ASK1 subsequently leads to activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38-MAPK, resulting in induction of cell death. JNK can also be inhibited by complex formation with glutathione S-transferase-π (GST-π) under nonstressed conditions, and can be activated by ROS in a similar fashion as ASK1. Negative regulatory molecules include the Ser/Thr phosphatase 5 (PP5), which inhibits ASK1 kinase activity by causing its dephosphorylation, and heat-shock protein 72 (Hsp72), which inhibits JNK activity. *Site of redox regulation. Grey, Active forms of the proteins.
