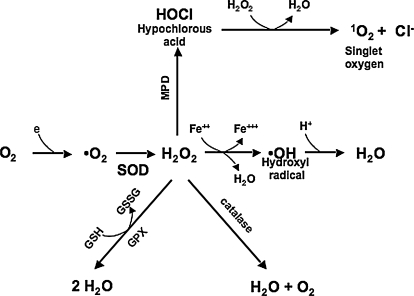
FIG. 1.
Reactive oxygen species. Cells generate aerobic energy by reducing molecular oxygen (O2) to water. During the metabolism of oxygen, superoxide (−O2) is occasionally formed. Superoxide is rapidly dismutated to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is converted by glutathione peroxidase or catalase to water. MPD (myeloperoxidase) converts H2O2 in neutrophils to hypochlorous acid (HOCl), a strong oxidant that acts as a bactericidal agent in phagocytic cells. During a Fenton reaction, H2O2 is converted in a spontaneous reaction catalyzed by Fe2+ to the highly reactive hydroxyl radical ·OH.