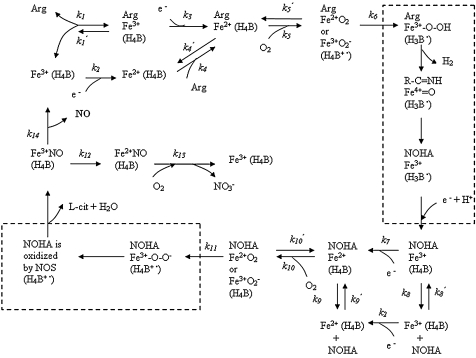
FIG. 3.
Mechanism for the formation of NO via eNOS catalysis after the binding of the coenzyme tetrahydrobiopterin (H4B). The heme iron (Fe) is the major catalytic site and represents NOS3 here. NOS3 undergoes a series of redox reactions. Arg represents l-arginine, and NOHA represents Nω-hydroxyl-l-arginine. Parentheses around H4B, H4B+•, or H3B• mean that that species is bound to the enzyme. NO is released from Fe3+NO. All three NOS isoforms share a similar catalytic mechanism. [Adapted from (66, 85).]