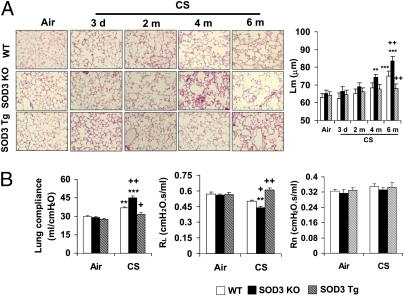
Fig. 1.
SOD3 attenuated CS-induced airspace enlargement and lung function decline. SOD3 KO, SOD3 Tg, and WT mice were exposed to CS for 3 d to 6 mo (m), and killed at 24 h following their last exposure. (A) SOD3 KO mice were susceptible to develop airspace enlargement whereas overexpression of SOD3 attenuated increased Lm of airspace in response to chronic CS exposure. H&E-stained pictures represent three separate experiments. Original magnification, 100×. (B) Overexpression of SOD3 restored the abnormal increase of lung compliance in mice exposed to CS for 6 mo. SOD3 exhibited a protective effect on RL, although 6-mo CS exposure showed only a decreasing trend in RL in WT mice. However, Rn was not altered by either CS exposure or SOD3. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3–4 per group). **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus the corresponding air-exposed groups; +P < 0.05 and ++P < 0.01 versus the corresponding CS-exposed WT mice.