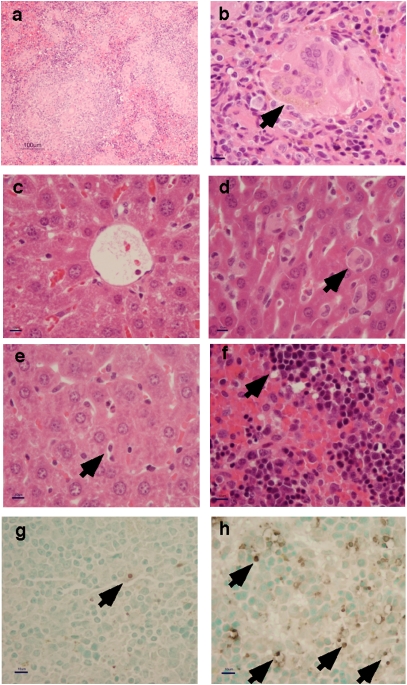
Fig. 2.
Pathology of typhoid in hu-SRC-SCID mice. (A) Granulomatous inflammation with mononuclear cell infiltration in the spleen of an infected hu-SRC-SCID mouse after 48–72 h. (B) Multinucleated giant cell (arrow) in the spleen of an infected hu-SRC-SCID mouse. (C) Central lobular hepatocellular changes in the liver of an infected hu-SRC-SCID mouse. (D) Kupffer cell swelling (arrow) in the liver of an infected hu-SRC-SCID mouse. (E) Mild hepatocellular changes with normal-appearing Kupffer cells (arrow) in the liver of an infected control NOD-scid IL2rγnull mouse. (F) Pyknotic lymphocytes (arrow) with cytoplasmic shrinkage in the spleen of an infected hu-SRC-SCID mouse. (G) Low background levels of cell death (arrow) visualized by TUNEL straining in the spleen of an infected control NOD-scid IL2rγnull mouse. (H) Increased cell death (arrows) visualized by TUNEL staining in the spleen of an infected hu-SRC-SCID mouse. (Magnification: A, 100×; B–H, 400×; scale bar: A, 100 μm; B–H, 10 μm.)