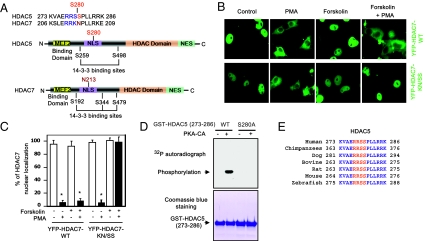
Fig. 2.
HDAC5 is a substrate for PKA. (A) (Upper) Comparison of amino acids surrounding the regulatory serine (arrowhead) between HDAC5 and HDAC7. (Lower) Schematic diagram of the HDAC5 and HDAC7 functional domains. (B and C) Nuclear export of YFP-HDAC7-WT is resistant to forskolin treatment, but nuclear export of YFP-HDAC7-K196S/N197S (mouse sequence) mutant was inhibited by forskolin in Cos7. *, P < 0.05 versus without PMA; n = 5. (D) (Upper) 32P autoradiograph image from in vitro kinase assays performed with recombinant PKA-CA and GST-HDAC5-WT (273–286) or GST-HDAC5-S280A (273–286) peptides. (Lower) The equal loading of GST proteins was shown by Coomassie blue staining. (E) Cos7 cells were transfected with Flag-tagged HDAC5-WT or Flag-tagged HDAC5-S280A and then were treated with forskolin (10 μM) at different times. Phosphorylation of HDAC5 in cell lysates was detected by immunoblotting with PKA phospho-substrate antibodies after immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibodies. (E) Alignment of amino acid sequences surrounding HDAC5 S280 in various species.