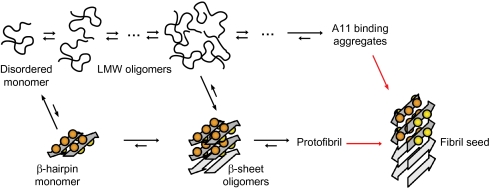
Fig. 5.
Aβ aggregation via two pathways. One pathway involves LMW oligomers without regular secondary structure and eventually large nonfibrillar aggregates binding the A11 antibody (coil pathway; Upper) and the other involves assembly into β-sheet oligomers, or coil oligomers that are converted into β-sheet oligomers, which are building blocks of mAb158 binding protofibrils (β-sheet pathway; Lower). Neurotoxic Aβ aggregates are formed along the β-sheet pathway. The scheme is consistent with the present studies of Aβcc and overall features can be reconciled with a large body of work on wild-type and naturally occurring Aβ mutants as discussed in the text. Red arrows reflect the interconversion of Aβ subunits from β-hairpin conformation in soluble aggregates to cross-β structure in fibril seeds and mature amyloid fibrils.