Table 8. 10-year total coronary heart disease rates in men and women by Framingham Risk Category and Ankle Brachial Index at baseline for all studies1 combined in the ABI Collaboration.
| Ankle Brachial Index: | ≤ 0.90 | 0.91 to 1.10 | 1.11 to 1.40 | >1.40 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Coronary Heart Disease3 % (n) | |||||
| Men | |||||
| Framingham Risk Category2 | |||||
| Low <10% | 8 (76) | 5 (1076) | 4 (4255) | 5 (236) | 5 (5643) |
| Intermediate 10-19% | 16 (245) | 12 (2069) | 12 (4815) | 8 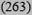
|
13 (7392) |
| High ≥20% | 40 (1149) | 21 (3406) | 18 
|
14 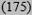
|
23 (8398) |
| Women | |||||
| Framingham Risk Category2 | |||||
| Low <10% | 21 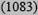
|
10 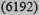
|
9 (7909) | 11 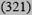
|
11 (15505) |
| Intermediate 10-19% | 25 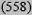
|
12 (2429) | 11 (2433) | 13 (143) | 13 (5563) |
| High ≥20% | 44 (200) | 21 (598) | 22 (577) | 34 (43) | 27 (1418) |
Excluding Health in Men, Hoorn and InCHIANTI studies, in which non-fatal events unavailable.
Categories of predicted 10-year % incidence of coronary heart disease, including coronary death, myocardial infarction and angina.
Total coronary heart disease, including coronary death, myocardial infarction and angina. Rates are approximate based on observed major coronary events (coronary death or myocardial infarction) adjusted by established conversion factors.26
The n between the brackets are the total number of subjects in each cell with the specified Framingham Risk Category and ABI level, irrespective of whether they did or did not have coronary heart disease.
Shaded numbers indicate subjects who would change between low (<10%), intermediate (10-19%) and high (≥20%) risk categories from that predicted by Framingham Risk Score when ABI included.
Analysis based on random effects pooling of Kaplan-Meier estimates from the individual studies
