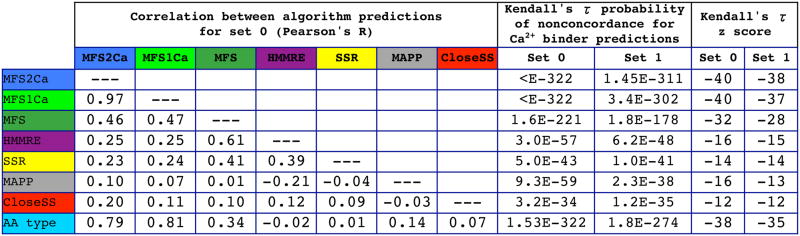
Figure 4.
Predictive algorithms with low correlation can have additive value. The Pearson’s R correlation coefficients between predictions of individual methods are relatively low, with the maximum for HMMRE and SSR being 0.39. Predictions of the novel CloseSS and sMAPP algorithm have low correlation to those of others, maximally correlated to HMMRE as 0.12 and 0.21 absolute, respectively. At right: Statistical significance of prediction concordance demonstrates predictive ability for an algorithm. Kendall’s τ is used to assess the null hypothesis of nonconcordance between true positive calcium binders or nonbinders and algorithm predictions (scores are considered without use of a threshold). All algorithms considered here are significant at levels beyond p<10−30. The novel algorithms we propose here are significant predictors of calcium binder versus nonbinder residues, and display low correlation to existing algorithms. Thus the HMMRE, SSR, sMAPP, CloseSS, and amino acid type scores might be synergistically combined into MFS2Ca, as verified in Figures 2 and 3.