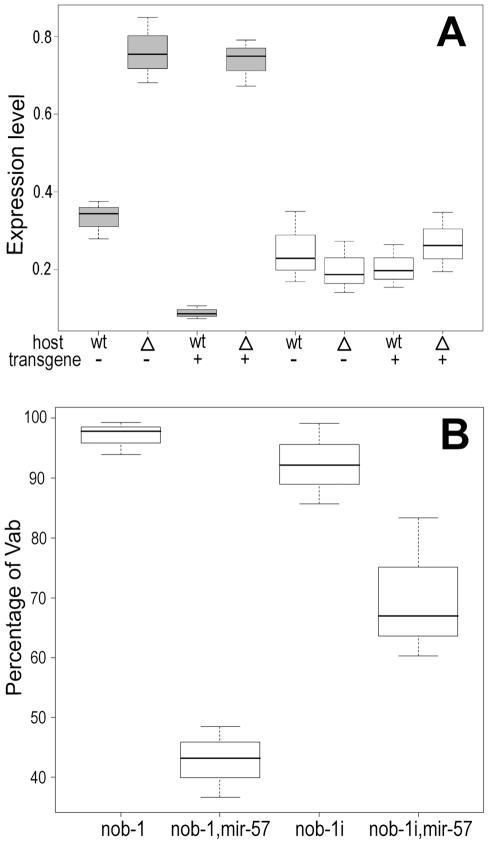
Figure 9. Genetic interactions between nob-1 and mir-57.
(A) Real time RT-PCR assay of nob-1a (white) and nob-1b (grey) transcripts in the presence (wt) or absence (Δ) of genomic mir-57. Deletion of genomic mir-57 increases nob-1b transcripts about two-fold while no effects were observed for nob-1a transcript level. The nob-1b transcript level is roughly four-fold lower in mir-57 promoter-array wild type strain (+) than that in wild type only (−). (B) The percentage of Vab animals is plotted for mutants or RNAi of nob-1 in the presence or absence of genomic mir-57. The left two of experiments contrast the phenotypes of nob-1(ct230) and nob-1(ct230); mir-57(gk175), whereas the right two contrast nob-1(RNAi); and nob-1(RNAi); mir-57(gk175). The fraction of nob-1 mutant animals exhibiting abnormal tail phenotypes is reduced in both cases by the removal of the genomic mir-57.