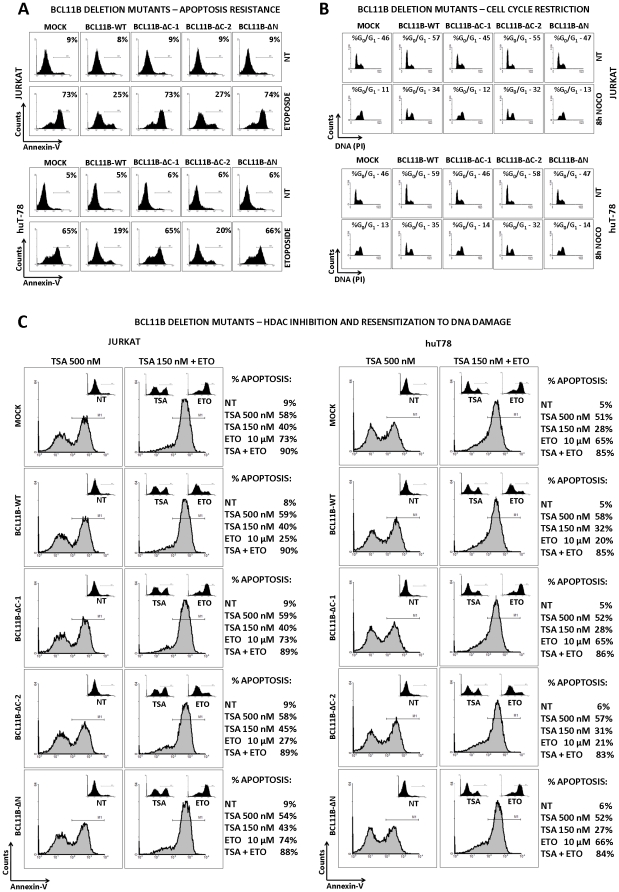
Figure 7. Bcl11b truncated mutants: apoptosis resistance, cell cycle retardation and HDAC dependence.
(A) Jurkat and huT-78 cells transduced with the empty vector (mock) and constructs encoding the full-length or truncated BCL11B variants were exposed to etoposide for 6h after which the viability was analyzed by Annexin-V binding assay. (B) The T cell lines expressing endogenous (mock), enforced (BCL11B-WT) and truncated BCL11B (Δ) were synchronized at G2/M phase of cell cycle using mitosis inhibitor nocodazole (0,5 µM). The effect of elevated Bcl11b and Bcl11b-derived mutant proteins on cell cycle was analyzed before and 8h after initiation of nocodazole treatment. The cell cycle distribution was analyzed by propidium iodide (PI) staining of genomic DNA followed by FACS measurement of PI fluorescence. (C) Jurkat and huT-78 cells transduced with empty or BCL11B-encoding vectors (wild-type and truncated) were treated for with high dose of histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA, left panels) or left untreated (insets). In addition, a lower dose of TSA (150 nM) was combined with the standard etoposide treatment (right panels). The treatments with TSA- and etoposide-only were performed for comparison (insets). The effects of the drugs on the viability of cells expressing endogenous, elevated and truncated Bcl11b was measured with Annexin-V binding assay followed by FACS quantification. The data displayed here represent results obtained from one of at least three separate experiments.