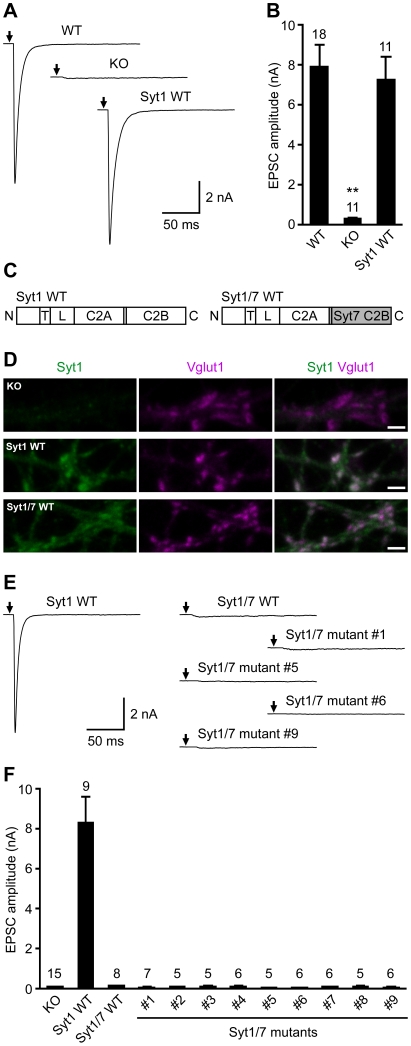
Figure 1. The synapotagmin-7 C2B domain cannot replace the synapotagmin-1 C2B domain to trigger Ca2+-evoked fast neurotransmitter release in hippocampal neurons.
(A,B) Ca2+-triggered fast neurotransmitter release in wild-type neurons (WT), synapotagmin-1 knockout neurons (KO), and KO neurons rescued by WT synapotagmin-1 (Syt1 WT). (A) Exemplary traces showing the evoked EPSCs. The arrows represent stimulations; artifacts and action potentials are blanked. (B) Bar graphs showing the summary data of EPSC amplitudes. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. The numbers of neurons analyzed are shown above the bars. **, P<0.001 compared to WT or Syt1 WT, one-way analysis of variance. (C) Schematic diagrams illustrating the domain structures of WT synapotagmin-1 (Syt1 WT) and a chimeric synapotagmin-1/7 (Syt1/7 WT) in which the synapotagmin-1 C2B domain (residues 266–421) is replaced by the synapotagmin-7 C2B domain (residues 260–403). N, N terminus; T, transmembrane domain; L, linker region; C, C terminus. (D) Exemplary confocal images showing the presynaptic localization of Syt1 WT and Syt1/7 WT in synapotagmin-1 KO neurons. Neurons were immunostained with antibodies against the N-terminal portion of the synaptotagmin-1 C2A domain (green images), Vglut1 (magenta images), and EGFP (not shown). The merged images show the presence of synaptotagmin-1 WT and Syt1/7 WT in the presynaptic termini identified by Vglut1. Scale bars: 2 µm. (E,F) Ca2+-triggered fast neurotransmitter release in synapotagmin-1 KO neurons rescued by Syt1 WT or chimeric Syt1/7 variants. The details of the Syt1/7 chimeric constructs are shown in Figure 2C. (E) Exemplary traces showing the evoked EPSCs. The arrows represent stimulations; artifacts and action potentials are blanked. (F) Bar graphs showing the summary data of EPSC amplitudes. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. The numbers of neurons analyzed are shown above the bars. None of the chimeric Syt1/7 variants is able to restore the diminished EPSC amplitude of synapotagmin-1 KO neurons (P<0.001 compared to Syt1 WT, one-way analysis of variance).