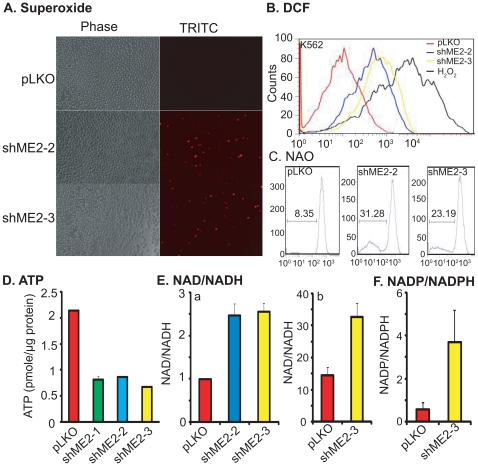
Figure 4. Depletion of endogenous ME2 enhances ROS generation, increases NAD+/NADH and NADP/NADPH ratios and decreases ATP levels.
A: Accumulation of mitochondrially generated superoxide in K562 ME2 knockdown cells as detected by MitoSOX. Data are representative of two independent experiments. B: Increased ROS in K562 ME2 knockdown cells detected by flow cytometry using CM-H2DCF-DA. Each histogram is representative of three experiments. C. Comparison of oxidative damage to cardiolipin in ME2 knockdown versus control K562 cells. M1 indicates subpopulation of cells that lost NAO signal due to cardiolipin oxidation. D. Depletion of ME2 inhibits ATP production in K562 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 3. E: Depletion of ME2 increases NAD+/NADH ratio. a, NAD+ and NADH were measured by NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Abcam, San Francisco, CA) as described in “Materials and Methods”. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 3. b, NAD+ and NADH were measured by LC-MS methods as described in “Materials and Methods”. F. Depletion of ME2 increases NADP/NADPH ratio in ME2 knockdown cells. NADP and NADPH were measured by LC-MS methods as described in “Materials and Methods”.