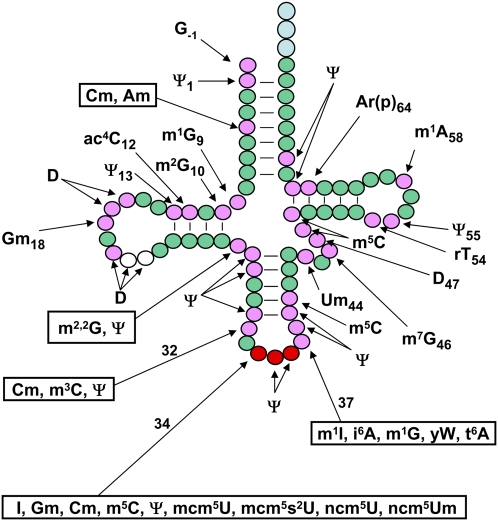
Figure 1.
A schematic of modifications found in cytoplasmic tRNA in S. cerevisiae. tRNA is shown in its usual secondary structure form, with circles representing nucleotides and lines representing base pairs. (Green circles) Residues that are unmodified in all yeast tRNA species; (pink circles) residues that are modified in some or all tRNA species; (white circles) additional residues (20a and 20b) that are present in some, but not all, tRNAs and are sometimes modified; (red circles) anticodon residues, which are modified in some tRNAs; (light-blue circles) the CCA end. Conventional abbreviations are used; see the Modomics database (http://modomics.genesilico.pl). (Ψ) Pseudouridine; (Am) 2′-O-methyladenosine; (Cm) 2′-O-methylcytidine; (m1G) 1-methylguanosine; (m2G) 2-methylguanosine; (ac4C) 4-acetylcytidine; (D) dihydrouridine; (Gm) 2′-O-methylguanosine; (m2,2G) N2,N2-dimethylguanosine; (m3C) 3-methylcytidine; (I) inosine; (m5C) 5-methylcytidine; (mcm5U) 5-methoxycarbonylmethyluridine; (mcm5s2U) 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thiouridine; (ncm5U) 5-carbamoylmethyluridine; (ncm5Um) 5-carbamoylmethyl-2′-O-methyluridine; (m1I) 1-methylinosine; (i6A) N6-isopentenyl adenosine; (yW) wybutosine; (t6A) N6-threonylcarbamoyladenosine; (Um) 2′-O-methyluridine; (m7G) 7-methylguanosine; (rT) ribothymidine; [Ar(p)] 2′-O-ribosyladenosine (phosphate). The pictured molecule starts at position −1 and is numbered consecutively from the next base (+1) to 76 (with the insertion of two residues [20a and 20b]). Several tRNA species have a longer variable arm starting after residue 44, and some tRNAs have different numbers of residues in the D-loop and the variable arm, but the anticodon is always numbered residues 34, 35, and 36, and the CCA end is always numbered residues 74, 75, and 76.