Figure 2.
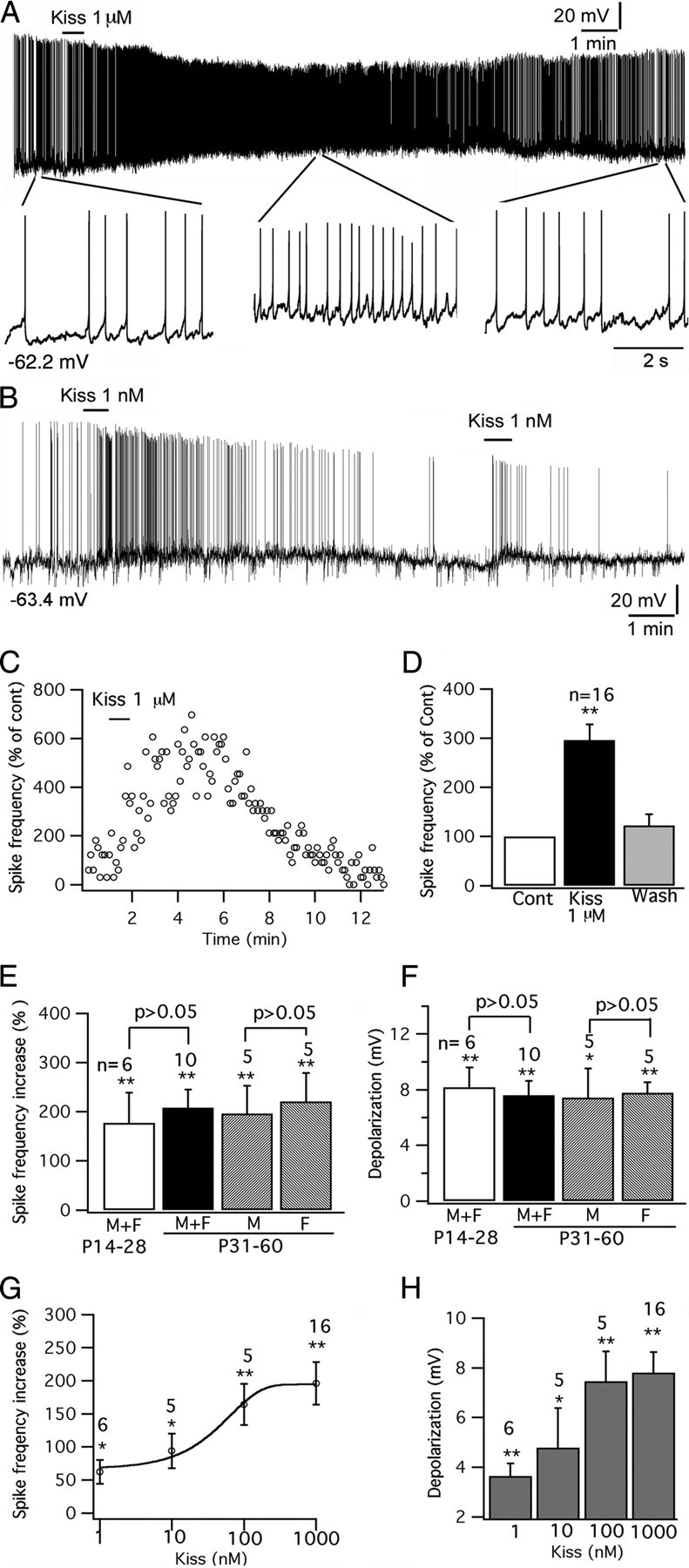
Kisspeptin excites POMC neurons. A, A trace showing that kisspeptin (1 μm) excited POMC neurons, with segments of the trace amplified below. B, Trace showing excitation of 1 nm kisspeptin on POMC cells, and this effect was repeated by a second application of kisspeptin on the same cell. C, Time course of the effect of kisspeptin on the POMC cell shown in trace in A. D, Bar graph showing the reversible increase of kisspeptin on the spike frequency of POMC cells with an average washout period of 10 min. E, Kisspeptin (1 μm) increases spike frequency in POMC cells in male and female mice at different ages. F, Depolarization of POMC cells by kisspeptin (1 μm) in male and female mice at different ages. G, The dose-dependent effect of kisspeptin on spike frequency of POMC cells. H, Bar graph showing the depolarization of membrane after application of kisspeptin from 1 nm to 1 μm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus control analyzed by ANOVA. The statistical tests used in comparing different ages or genders are grouped t tests. The number of cells tested is shown above the bars in E–H. The membrane potential values under the traces in A and B indicate the membrane potentials before applying kisspeptin. Error bars indicate SEM.
