Figure 4.
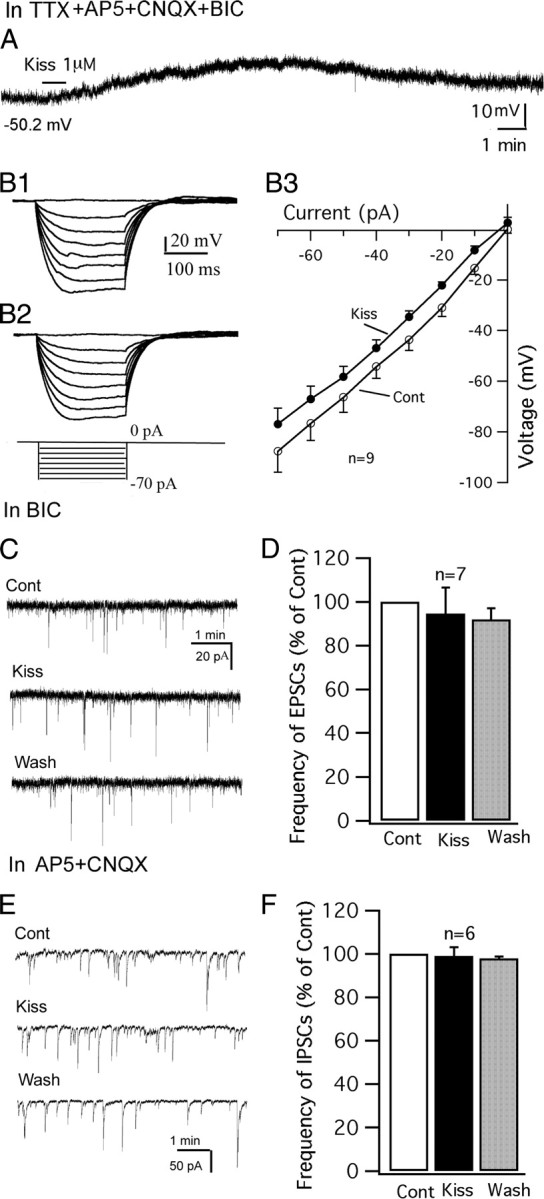
Direct effect of kisspeptin on POMC neurons. A, In the presence of TTX (0.5 μm), AP5 (50 μm), CNQX (10 μm), and BIC (30 μm), kisspeptin (1 μm) depolarized a POMC cell. The membrane potential value under the trace indicates the membrane potential before applying kisspeptin. B1–B3, Responses of a POMC cell to current injection from −70 to 0 pA before (B1) and during (B2) application of kisspeptin (1 μm) and the current–voltage relationship of POMC cells before and during kisspeptin (1 μm) (B3). C, Spontaneous EPSCs of a POMC cell during control, kisspeptin (1 μm), and washout period. EPSCs were recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV in the presence of BIC (30 μm). D, Bar graph showing that kisspeptin does not change the frequency of EPSCs. E, Spontaneous IPSCs of a POMC cell during control, kisspeptin (1 μm), and washout period. IPSCs were recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV in the presence of AP5 (50 μm) and CNQX (10 μm). F, Bar graph showing that kisspeptin does not change the frequency of IPSCs. Error bars indicate SEM.
