FIG. 2.
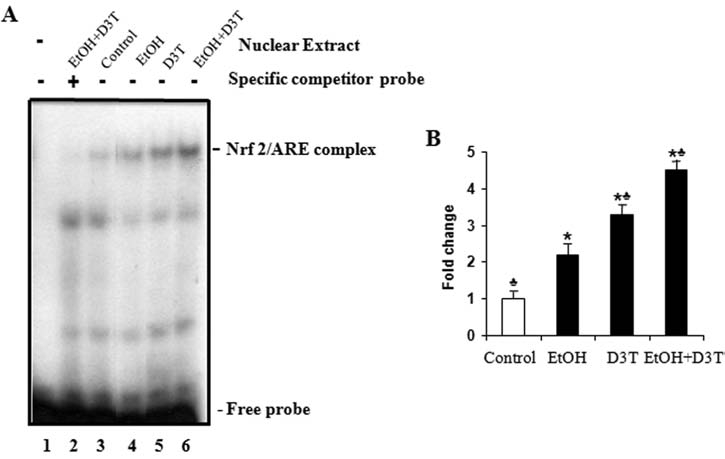
Ethanol and D3T exposure increase the Nrf2-ARE binding activity in mouse embryos. Nrf2-ARE binding was determined by using an EMSA with oligonucleotide probe for GCLC ARE in mouse embryos 6 h after exposure to ethanol. Embryo lysates were prepared from whole embryos treated with vegetable oil (Control), 2.9 g/kg ethanol (EtOH), pretreated with 5 mg/kg D3T alone (D3T), or treated with both ethanol and D3T (EtOH+D3T). (A) A representative gel-shift image. Lane 1, No nuclear extract. Lane 2, Nuclear extracts of embryos treated with ethanol and D3T in the presence of excess specific competitor probe. Lanes 3–6, Nuclear extracts of control and treated mouse embryos in the presence of labeled probe for GCLC ARE. (B) Bars represent the average values of the Nrf2-ARE binding activity of three gel-shift assays. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three separate experiments. *p < 0.05 vs. control. ♣ p < 0.05 vs. EtOH.
