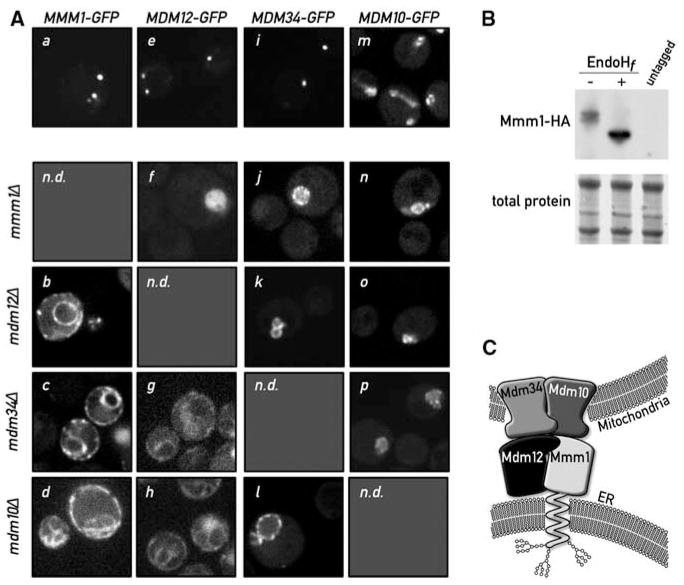
Fig. 3.
Mmm1 is an integral ER protein. (A) Disruption of a single ERMES component causes disassembly of the complex. Mmm1-GFP is localized in punctate structures in WT cells (a). Upon deletion of MDM12 (b), MDM34 (c), or MDM10 (d), Mmm1-GFP relocalizes to the ER. Mdm12-GFP displays a punctate pattern in WT cells (e). In the absence of Mmm1 (f), Mdm12-GFP displays a uniform mitochondrial localization (note the rounded swollen mitochondrial shape in mmm1Δ strains), but in the absence of MDM34 (g) or MDM10 (h), Mdm12-GFP relocalizes to the ER. Mdm34-GFP is also in punctate structures in WT cells (i). Upon mutation of any other complex member, Mdm34 relocalizes more uniformly to the mitochondrial membrane (j, k, l). Mdm10-GFP localizes to the whole surface of the mitochondria (m) and localizes to the rounded mitochondria after deletion of any other ERMES component (n, o, p). n.d., not determined. (B) Mmm1 is N-glycosylated. Whole-cell extract from a strain bearing a functional HA-tagged MMM1 gene was subjected to SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with or without pretreatment with the glycosidase EndoHf. Detection was performed by Western blotting with an anti-HA antibody. The shift in electrophoretic mobility upon glycosidase treatment is indicative that Mmm1 is N-linked glycosylated. (C) Model of ERMES-mediated ER-mitochondria tethering. Mmm1 is an integral ER protein glycosylated on its N-terminal side. Mmm1 interacts with Mdm10, a OMM β-barrel protein. Mdm34 and Mdm12 promote this association, most probably via direct association.