Figure 4.
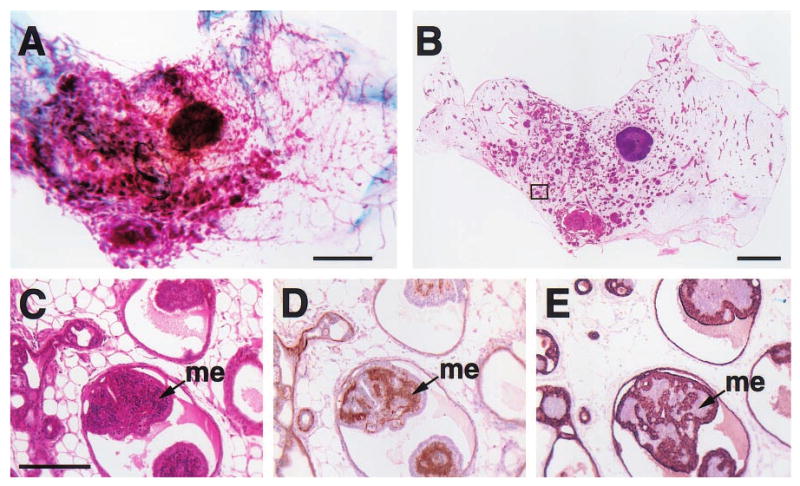
Histologic appearance of a florid papillary hyperplasia (intraductal papillomatosis) in the mammary gland of a 2-year-old virgin WAP-Str1 transgenic mouse as seen by wholemount (a), H&E (b,c), anti-smooth muscle actin (d) and anti-cytokeratin-8 (e) staining. The area outlined in (b) is shown at higher magnification in (c – e). The small, basophilic cells within the papillary projections (me) are smooth muscle actin-positive (d) and cytokeratin-8-negative (e), indicating the abnormal, internal presence of myoepithelial cells. Although small focal collections of lymphocytes were present (not shown), fibrosis was not observed and the far ends of the gland were essentially normal. Scale bars, 2 mm (a,b), 200 μm (c – e)
