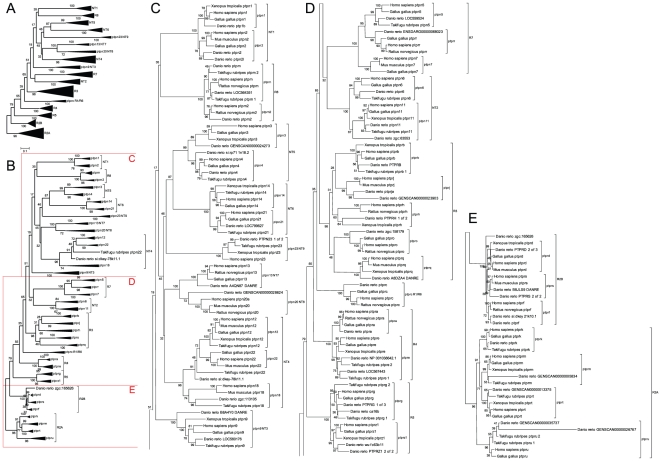
Figure 1. Alignment of vertebrate PTP domains.
Protein sequences were obtained from Ensembl database of all PTPs from zebrafish, Fugu, Xenopus, chicken, mouse, rat and human. The PTP domains were identified using http://www.expasy.org/prosite/ and used for alignment using the MEGA4 program. When a tandem PTP domain was present, the D1 PTP domain was used for the alignment. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 31.88069250 is shown. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Dayhoff matrix based method and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. All positions containing alignment gaps and missing data were eliminated only in pairwise sequence comparisons (Pairwise deletion option). There were a total of 475 positions in the final dataset (Tamura et al. 2007). An overview of the entire collapsed tree is shown in Figure 1A, with individual pieces split to make up figures 1B–E, as indicated. Not all known annotated genes of species other than zebrafish are included.