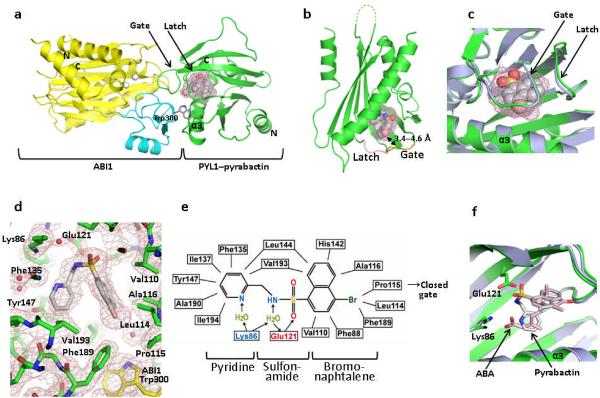
Figure 2.
Structure of the PYL1–pyrabactin–ABI1 complex. (a) Structure overview of the complex. The N- and C- termini of PYL1 and ABI1, the locking residue Trp300, and the PYL1 α3-helix are indicated. Pyrabactin is shown as ball representation with the surrounding ligand binding pocket as mesh. (b) Structure of pyrabactin as ball model in the PYL1 pocket are shown as mesh. The gate and latch are shown in yellow and magenta with the gate–pyrabactin distance indicated. (c) Close view of the pyrabactin-bound PYL1 ligand binding pocket (green) overlaid with the PYL1 structure in the PYL1–ABA–ABI1 complex (blue-grey). (d) 2 F0−Fc electron density map of bound pyrabactin and its surrounding residues contoured at 1.0 σ. (e) Schematic representation of the interactions between pyrabactin and PYL1 binding pocket residues. Charged interactions and hydrogen bonds are indicated by arrows, hydrophobic interactions by solid lines with hydrogen bond donors in blue and acceptors in red. The position of pyrabactin relative to the closed gate is indicated. (f) Overlay of pyrabactin (grey) with (+)-ABA (pink) in the PYL1 binding pocket.