Figure 3.
Zebrafish Eye Development Disturbed by Knockdown of znf513 Expression and Rescue of znf513 Morphants
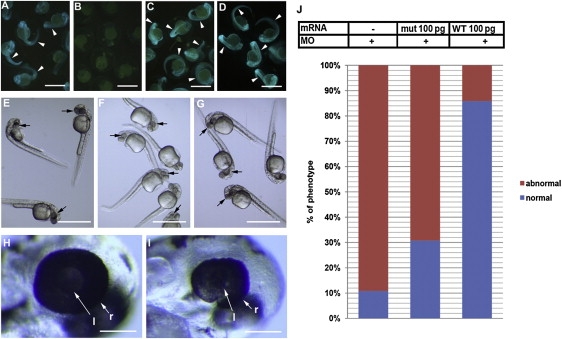
Morpholino-sensitive 5′-modified EGFP mRNA (A, B, C) or native unmodified EGFP (D) was injected to single cell stage embryos. znf513-MO (B, D, F, I), MM-MO (C, G, H), or injection buffer (E) was injected into embryos.
(A–D) Validation of the activity of znf513-MO on the expression of znf513. znf513-MO injection eliminated the fluorescence signal (green on the embryo body, arrowheads) from coinjected morpholino-sensitive 5′-modified EGFP mRNA (B), and it did not reduce the expression of native unmodified EGFP without the znf513 sequence (D). MM-MO had no effect on morpholino-sensitive GFP expression (C). Note that all embryos contain faint yellowish autofluorescence in the egg yolk not derived from EGFP.
(E–G) 0.5 ng Znf513-MO (F) dramatically reduced eye size (black arrows) compared to MM-MO-injected (G) and buffer-injected (E) embryos.
(H and I) Higher magnification of the heads from embryos shown in (G) and (F) showing reduced size of the retina in a znf513-MO-injected embryo relative to a MM-MO-injected embryo (l, lens; r, retina, white arrows).
(J) Graph depicting proportions of embryos with abnormal phenotype (eye size) associated with znf513-MO injection and rescue by coinjected znf513 mut and WT mRNA.
(A–D) 24 hpf, (E–I) 37 hpf. Scale bars represent 1 mm in (A)–(G) and 100 μm in (H) and (I).
