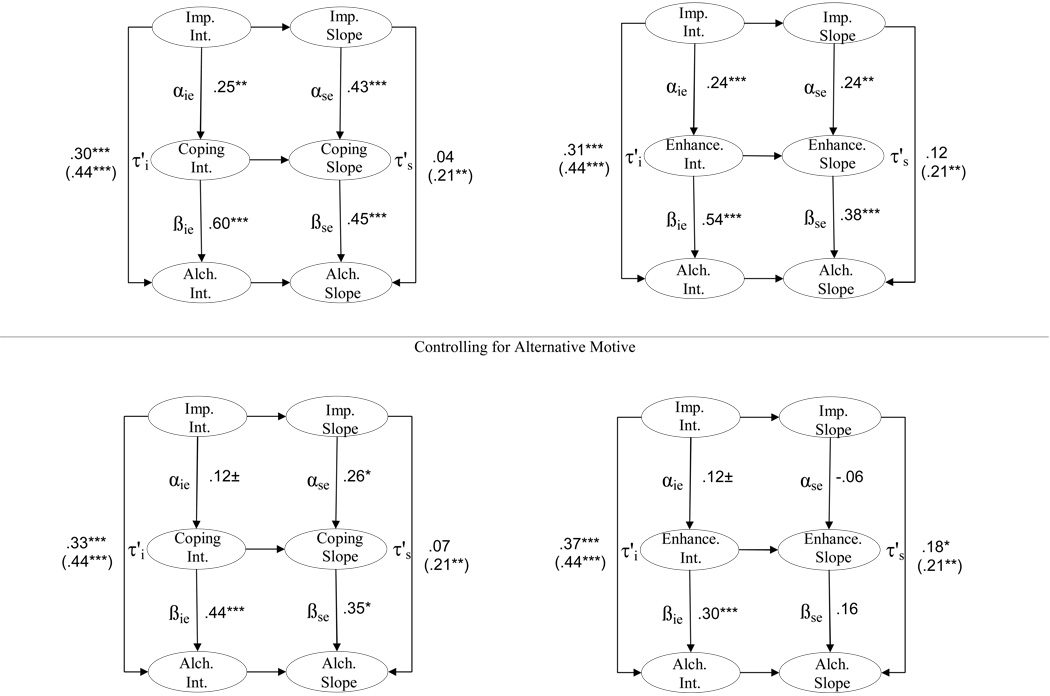
Figure 4. Parallel Process Latent Growth Models of Impulsivity, Drinking Motives, and Alcohol Problems.
Imp. = impulsivity. Enhance = Enhancement. Alch. = Alcohol Problems. Direct Effect of Initial Level (age 18) of Impulsivity on Initial Level of Alcohol Problems= τ'i. Direct Effect of Impulsivity Change on Change in Alcohol Problems= τ's. All within-construct and across-construct paths were estimated but not presented. Total effects between impulsivity and alcohol problems are displayed in parentheses. All variables were controlled for family history of alcoholism and sex. The results presented in the bottom panel included these additional specifications: coping intercept was controlled for enhancement intercept. Coping slope was controlled for enhancement intercept and slope. Enhancement intercept was controlled for coping intercept. Enhancement slope was controlled for coping intercept and slope. ±p<.10, *p<.05, **p<.01,***p<.001.