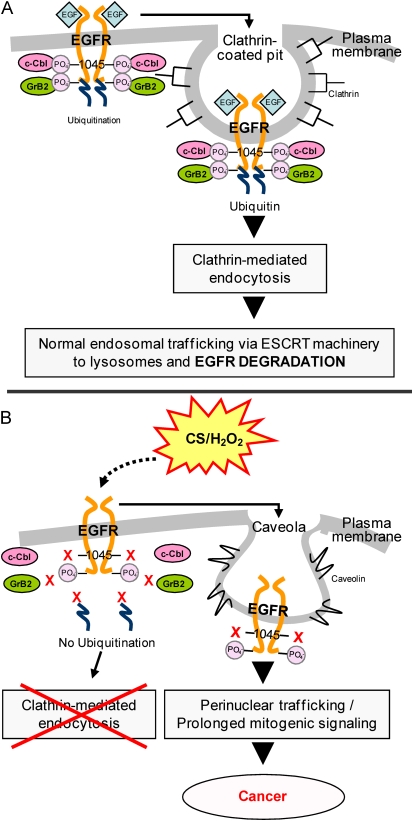
Figure 3.
Proposed model of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) aberrant activation and trafficking in the setting of cigarette smoke (CS). (A) Under EGF exposure, c-Cbl can bind directly and indirectly to the EGFR via phospho-Tyr-1045 and Grb2, respectively, allowing receptor ubiquitination, clathrin-mediated endocytosis, and lysosomal degradation. (B) Under cigarette smoke exposure, EGFR Tyr-1045 is not phosphorylated and c-Cbl can no longer interact with EGFR; therefore, the receptor does not follow the same degradation pathway that is induced by EGF. Instead, the EGFR is stabilized at the plasma membrane and also trafficks to a perinuclear compartment where it remains active and contributes to prolonged signaling.