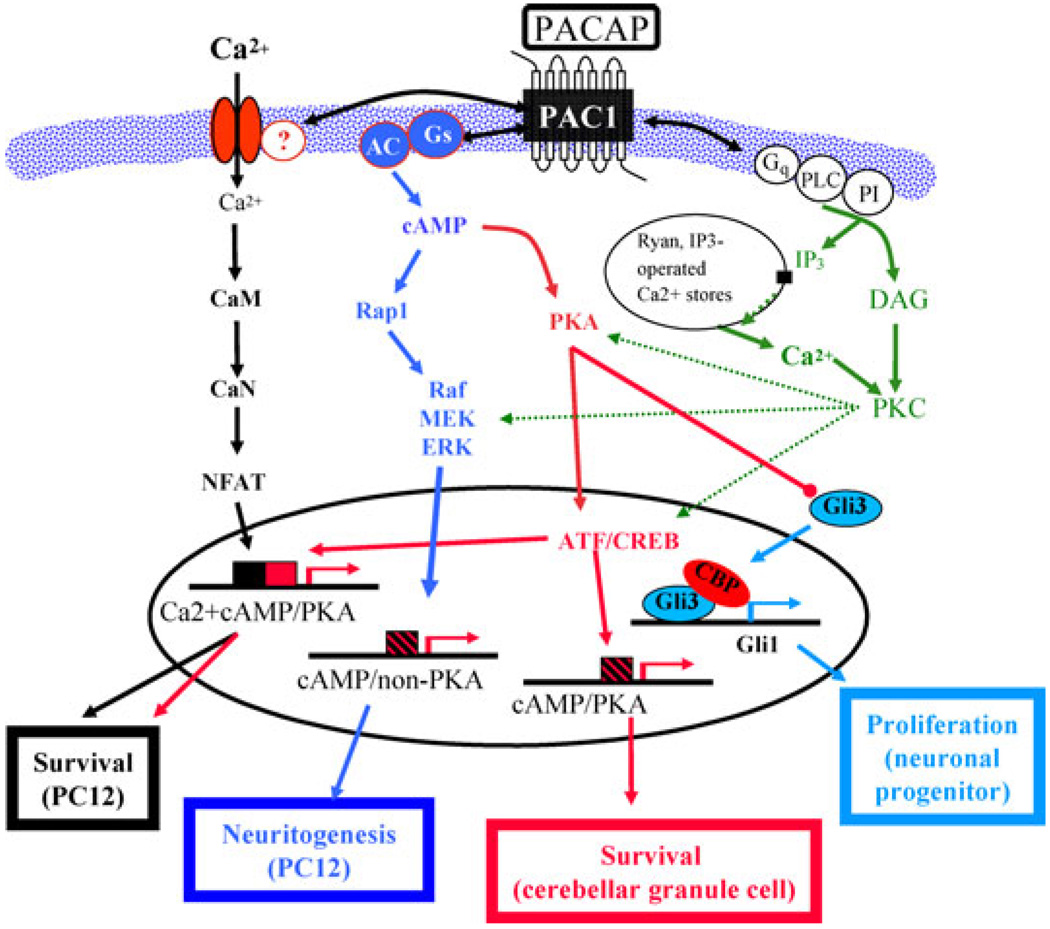
Figure 4.
Implications of PC12 cell microarray/transcriptome analysis for pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) actions, and PACAP-activated signaling pathways, in vivo. Depiction of pathways leading to cell survival, neuritogenesis, and proliferation/growth arrest in PC12 cells in vitro and in neurons and neuronal progenitor cells in vitro and in vivo. Only the portion of the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway for cell proliferation through which PACAP modulation is thought to occur50 is shown. Note that both canonical (protein kinase A [PKA] -dependent) and noncanonical (cyclic adenosine monophosphate [cAMP] -dependent, PKA-independent) signaling pathways may exist separately or together, and that either type of calcium-dependent signaling may also coexist with either of these two pathways, depending on cell type. (Adapted from Chen et al.14)