Figure 1.
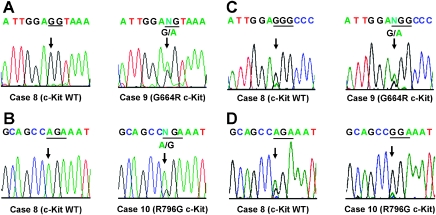
KIT mutations in tumor samples from sporadic ACC. (A) Genomic DNA electropherograms of case 8 (left) and case 9 (right) are shown. They identify the KIT missense mutation in exon 13. Case 8 has a wild-type (WT) sequence. Case 9 has nucleotide (nt) switches, specifically nt1990G → A in exon 13, with a predicted missense substitution of arginine for glycine 664 (G664R). The first and second nucleotides for codon 664 are highlighted with underlines. The third nucleotide is located in a different exon. (B) Genomic DNA electropherograms of case 8 (left) and case 10 (right) are shown, identifying the KIT missense mutation in exon 17. Case 8 has a WT sequence. Case 10 has an nt2386A → G transition in exon 17, with a predicted missense substitution of glycine for arginine 796 (R796G). Triplet nucleotides at codon 796 are marked with underlines. (C) RT-PCR products electropherograms of case 8 (left) and case 9 (right). Case 8 has a wild-type (WT) sequence. Case 9 has the KIT missense mutation in codon 664. Triplet nucleotides for codon 664 are highlighted with underlines. (D) RT-PCR products electropherograms of case 8 (left) and case 10 (right) RT-PCR products are shown. Case 8 has a wild-type (WT) sequence. Case 10 has the KIT missense mutation in codon 796. Triplet nucleotides for codon 796 are highlighted with underlines.